High-resolution transcriptional analysis of the regulatory influence of cell-to-cell signalling reveals novel genes that contribute to Xanthomonas phytopathogenesis
- PMID: 23617851
- PMCID: PMC3744752
- DOI: 10.1111/mmi.12229
High-resolution transcriptional analysis of the regulatory influence of cell-to-cell signalling reveals novel genes that contribute to Xanthomonas phytopathogenesis
Abstract
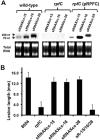
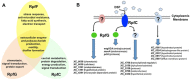
The bacterium Xanthomonas campestris is an economically important pathogen of many crop species and a model for the study of bacterial phytopathogenesis. In X. campestris, a regulatory system mediated by the signal molecule DSF controls virulence to plants. The synthesis and recognition of the DSF signal depends upon different Rpf proteins. DSF signal generation requires RpfF whereas signal perception and transduction depends upon a system comprising the sensor RpfC and regulator RpfG. Here we have addressed the action and role of Rpf/DSF signalling in phytopathogenesis by high-resolution transcriptional analysis coupled to functional genomics. We detected transcripts for many genes that were unidentified by previous computational analysis of the genome sequence. Novel transcribed regions included intergenic transcripts predicted as coding or non-coding as well as those that were antisense to coding sequences. In total, mutation of rpfF, rpfG and rpfC led to alteration in transcript levels (more than fourfold) of approximately 480 genes. The regulatory influence of RpfF and RpfC demonstrated considerable overlap. Contrary to expectation, the regulatory influence of RpfC and RpfG had limited overlap, indicating complexities of the Rpf signalling system. Importantly, functional analysis revealed over 160 new virulence factors within the group of Rpf-regulated genes.
© 2013 The Authors. Molecular Microbiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures



Comment in
-
RNA-Seq facilitates a new perspective on signal transduction and gene regulation in important plant pathogens.Mol Microbiol. 2013 Jun;88(6):1041-6. doi: 10.1111/mmi.12259. Epub 2013 May 22. Mol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23659691
References
-
- Chen X-L, Tang D-J, Jiang R-P, He Y-Q, Jiang B-L, Lu G-T, et al. sRNA-Xcc1, an integron-encoded transposon- and plasmid-transferred trans-acting sRNA, is under the positive control of the key virulence regulators HrpG and HrpX of Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris. RNA Biol. 2011;8:947–953. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

