B-Raf and the inhibitors: from bench to bedside
- PMID: 23617957
- PMCID: PMC3646677
- DOI: 10.1186/1756-8722-6-30
B-Raf and the inhibitors: from bench to bedside
Abstract
The B-Raf protein is a key signaling molecule in the mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway and has been implicated in the pathogenesis of a variety of cancers. An important V600E mutation has been identified and can cause constitutive B-Raf activation. Recent studies have evaluated a variety of small molecule inhibitors targeting B-Raf, including PLX4032/vemurafenib, dabrafenib, LGX818, GDC0879, XL281, ARQ736, PLX3603 (RO5212054), and RAF265. Therapeutic resistance has been identified and various mechanisms described. This review also discussed the current understanding of B-Raf signaling mechanism, methods of mutation detection, treatment strategies as well as potential methods of overcoming therapeutic resistance.
Figures
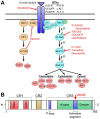

References
-
- Eychene A, Barnier JV, Apiou F, Dutrillaux B, Calothy G. Chromosomal assignment of two human B-raf(Rmil) proto-oncogene loci: B-raf-1 encoding the p94Braf/Rmil and B-raf-2, a processed pseudogene. Oncogene. 1992;7(8):1657–1660. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

