Diesel exhaust particles modify natural killer cell function and cytokine release
- PMID: 23618096
- PMCID: PMC3637383
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-8977-10-16
Diesel exhaust particles modify natural killer cell function and cytokine release
Abstract
Background: Natural killer (NK) cells are an important lymphocyte population in the nasal mucosa and play important roles in linking the innate and the adaptive immune response. Their two main functions are direct cell-mediated cytotoxicity and the release of cytokines. They are important during viral infections and cancer. Due to their location in the nasal mucosa, NK cells are likely exposed to inhaled pollutants, such as diesel exhaust. Whether and how exposure to diesel exhaust particles (DEP) affects NK cell function in the context of viral infections has not been investigated.
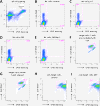
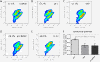
Methods: NK cells were isolated from peripheral blood obtained from normal healthy volunteers and subsequently stimulated with the viral mimetic polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid (pI:C), DEP, or pI:C+DEP for 18 hours. NK cells were subsequently analyzed for changes in surface marker expression, cytokine production, gene expression changes, and cytotoxic function using flow cytometry, ELISA, qRT-PCR, and cell-mediated cytotoxicity assay, respectively.
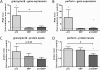
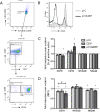
Results: Stimulation of NK cells with pI:C and pI:C+DEP, but not DEP alone, increased the release of IL-1β, IL-2, IL-4, IL-8, IL-10, IL-12p70, IFN-γ and TNF-α. As compared to pI:C alone or pI:C+DEP, the release of IL-1β, IL-8 and TNF-α was significantly lower after DEP stimulation alone. Stimulation with pI:C alone increased the gene and protein expression of granzyme B and perforin, which was completely blunted by adding DEP. Addition of DEP further reduced CD16 expression in pI:C stimulated cells. Similarly, cell-mediated cytotoxicity was significantly reduced by the addition of DEP.
Conclusions: In the context of viral infection, DEP potentially reduces NK cells' ability to kill virus-infected host cells, in spite of normal cytokine levels, and this may increase susceptibility to viral infections . This reduction in the potential ability of NK cells to kill virus-infected host cells may increase the susceptibility to viral infections after DEP exposure.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Diesel exposure suppresses natural killer cell function and resolution of eosinophil inflammation: a randomized controlled trial of exposure in allergic rhinitics.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016 May 6;13(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s12989-016-0135-7. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2016. PMID: 27154411 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diesel exhaust particles suppress in vivo IFN-gamma production by inhibiting cytokine effects on NK and NKT cells.J Immunol. 2004 Mar 15;172(6):3808-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.172.6.3808. J Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15004186
-
Comparison of inflammatory cytokine release from nasal epithelial cells of non-atopic non-rhinitic, allergic rhinitic and polyp subjects and effects of diesel exhaust particles in vitro.Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2017 Sep-Oct;45(5):473-481. doi: 10.1016/j.aller.2016.10.015. Epub 2017 Mar 2. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 2017. PMID: 28259510
-
Causation by Diesel Exhaust Particles of Endothelial Dysfunctions in Cytotoxicity, Pro-inflammation, Permeability, and Apoptosis Induced by ROS Generation.Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2017 Oct;17(4):384-392. doi: 10.1007/s12012-016-9364-0. Cardiovasc Toxicol. 2017. PMID: 26965709 Review.
-
Diesel Exhaust Particles and the Induction of Macrophage Activation and Dysfunction.Inflammation. 2018 Feb;41(1):356-363. doi: 10.1007/s10753-017-0682-6. Inflammation. 2018. PMID: 29047037 Review.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 infection, COVID-19 pathogenesis, and exposure to air pollution: What is the connection?Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021 Feb;1486(1):15-38. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14512. Epub 2020 Oct 6. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021. PMID: 33022781 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Broccoli Sprouts and Live Attenuated Influenza Virus on Peripheral Blood Natural Killer Cells: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 28;11(1):e0147742. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147742. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26820305 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Air Pollution: Possible Interaction between the Immune and Nervous System?Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 30;19(23):16037. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192316037. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36498110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Analysis of sphingosine kinase activity in single natural killer cells from peripheral blood.Integr Biol (Camb). 2015 Apr;7(4):392-401. doi: 10.1039/c5ib00007f. Integr Biol (Camb). 2015. PMID: 25786072 Free PMC article.
-
Diesel exhaust particle exposure in vitro impacts T lymphocyte phenotype and function.Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014 Dec 14;11:74. doi: 10.1186/s12989-014-0074-0. Part Fibre Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 25498254 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vivier E, Tomasello E, Baratin M, Walzer T, Ugolini S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat Immunol. 2008;9:503–510. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

