Dual-modality imaging with 99mTc and fluorescent indocyanine green using surface-modified silica nanoparticles for biopsy of the sentinel lymph node: an animal study
- PMID: 23618132
- PMCID: PMC3639813
- DOI: 10.1186/2191-219X-3-33
Dual-modality imaging with 99mTc and fluorescent indocyanine green using surface-modified silica nanoparticles for biopsy of the sentinel lymph node: an animal study
Abstract
Background: We propose a new approach to facilitate sentinel node biopsy examination by multimodality imaging in which radioactive and near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent nanoparticles depict deeply situated sentinel nodes and fluorescent nodes with anatomical resolution in the surgical field. For this purpose, we developed polyamidoamine (PAMAM)-coated silica nanoparticles loaded with technetium-99m (99mTc) and indocyanine green (ICG).
Methods: We conducted animal studies to test the feasibility and utility of this dual-modality imaging probe. The mean diameter of the PAMAM-coated silica nanoparticles was 30 to 50 nm, as evaluated from the images of transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy. The combined labeling with 99mTc and ICG was verified by thin-layer chromatography before each experiment. A volume of 0.1 ml of the nanoparticle solution (7.4 MBq, except for one rat that was injected with 3.7 MBq, and 1 μg of an ICG derivative [ICG-sulfo-OSu]) was injected submucosally into the tongue of six male Wistar rats.
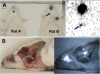
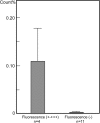
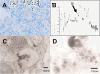
Results: Scintigraphic images showed increased accumulation of 99mTc in the neck of four of the six rats. Nineteen lymph nodes were identified in the dissected neck of the six rats, and a contact radiographic study showed three nodes with a marked increase in uptake and three nodes with a weak uptake. NIR fluorescence imaging provided real-time clear fluorescent images of the lymph nodes in the neck with anatomical resolution. Six lymph nodes showed weak (+) to strong (+++) fluorescence, whereas other lymph nodes showed no fluorescence. Nodes showing increased radioactivity coincided with the fluorescent nodes. The radioactivity of 15 excised lymph nodes from the four rats was assayed using a gamma well counter. Comparisons of the levels of radioactivity revealed a large difference between the high-fluorescence-intensity group (four lymph nodes; mean, 0.109% ± 0.067%) and the low- or no-fluorescence-intensity group (11 lymph nodes; mean, 0.001% ± 0.000%, p < 0.05). Transmission electron microscopy revealed that small black granules were localized to and dispersed within the cytoplasm of macrophages in the lymph nodes.
Conclusion: Although further studies are needed to determine the appropriate dose of the dual-imaging nanoparticle probe for effective sensitivity and safety, the results of this animal study revealed a novel method for improved node detection by a dual-modality approach for sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Figures
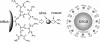



Similar articles
-
Comparing the hybrid fluorescent-radioactive tracer indocyanine green-99mTc-nanocolloid with 99mTc-nanocolloid for sentinel node identification: a validation study using lymphoscintigraphy and SPECT/CT.J Nucl Med. 2012 Jul;53(7):1034-40. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.112.103127. Epub 2012 May 29. J Nucl Med. 2012. PMID: 22645297
-
Sentinel lymphadenectomy in cervical cancer using near infrared fluorescence from indocyanine green combined with technetium-99m-nanocolloid.Lasers Surg Med. 2018 Dec;50(10):994-1001. doi: 10.1002/lsm.22999. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Lasers Surg Med. 2018. PMID: 29968916
-
[Diagnostic value of optical imaging combined with indocyanine green-guided sentinel lymph node biopsy in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis].Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019 Dec 25;22(12):1196-1204. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1671-0274.2019.12.017. Zhonghua Wei Chang Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31874538 Chinese.
-
Dual-Labeled Near-Infrared/(99m)Tc Imaging Probes Using PAMAM-Coated Silica Nanoparticles for the Imaging of HER2-Expressing Cancer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Jul 7;17(7):1086. doi: 10.3390/ijms17071086. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27399687 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic value of indocyanine green fluorescence guided sentinel lymph node biopsy in vulvar cancer: A systematic review.Gynecol Oncol. 2021 May;161(2):436-441. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2021.01.031. Epub 2021 Feb 5. Gynecol Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33551201
Cited by
-
Radiolabeled Dendrimers for Nuclear Medicine Applications.Molecules. 2017 Aug 25;22(9):1350. doi: 10.3390/molecules22091350. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28841180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoparticles and radiotracers: advances toward radionanomedicine.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2016 Nov;8(6):872-890. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1402. Epub 2016 Mar 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27006133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging indocyanine green-integrated nanocarriers for multimodal cancer therapy: a review.Nanoscale Adv. 2021 Apr 15;3(12):3332-3352. doi: 10.1039/d1na00059d. eCollection 2021 Jun 15. Nanoscale Adv. 2021. PMID: 36133722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Imaging of Metastatic Cancer Cells in Sentinel Lymph Nodes using Affibody Probes and Possibility of a Theranostic Approach.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Jan 19;20(2):427. doi: 10.3390/ijms20020427. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30669481 Free PMC article.
-
Indocyanine Green Nanoparticles: Are They Compelling for Cancer Treatment?Front Chem. 2020 Jul 16;8:535. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00535. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 32766203 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mariani G, Gipponi M, Moresco L, Villa G, Bartolomei M, Mazzarol G, Bagnara MC, Romanini A, Cafiero F, Paganelli G, Strauss HW. Radioguided sentinel lymph node biopsy in malignant cutaneous melanoma. J Nucl Med. 2002;3:811–27. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

