The Myb-p300-CREB axis modulates intestine homeostasis, radiosensitivity and tumorigenesis
- PMID: 23618903
- PMCID: PMC3641342
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.119
The Myb-p300-CREB axis modulates intestine homeostasis, radiosensitivity and tumorigenesis
Abstract
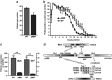
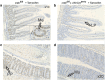
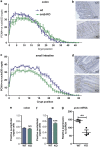
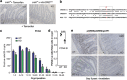
The gastrointestinal (GI) epithelium is constantly renewing, depending upon the intestinal stem cells (ISC) regulated by a spectrum of transcription factors (TFs), including Myb. We noted previously in mice with a p300 mutation (plt6) within the Myb-interaction-domain phenocopied Myb hypomorphic mutant mice with regard to thrombopoiesis, and here, changes in GI homeostasis. p300 is a transcriptional coactivator for many TFs, most prominently cyclic-AMP response element-binding protein (CREB), and also Myb. Studies have highlighted the importance of CREB in proliferation and radiosensitivity, but not in the GI. This prompted us to directly investigate the p300-Myb-CREB axis in the GI. Here, the role of CREB has been defined by generating GI-specific inducible creb knockout (KO) mice. KO mice show efficient and specific deletion of CREB, with no evident compensation by CREM and ATF1. Despite complete KO, only modest effects on proliferation, radiosensitivity and differentiation in the GI under homeostatic or stress conditions were evident, even though CREB target gene pcna (proliferating cell nuclear antigen) was downregulated. creb and p300 mutant lines show increased goblet cells, whereas a reduction in enteroendocrine cells was apparent only in the p300 line, further resembling the Myb hypomorphs. When propagated in vitro, crebKO ISC were defective in organoid formation, suggesting that the GI stroma compensates for CREB loss in vivo, unlike in MybKO studies. Thus, it appears that p300 regulates GI differentiation primarily through Myb, rather than CREB. Finally, active pCREB is elevated in colorectal cancer (CRC) cells and adenomas, and is required for the expression of drug transporter, MRP2, associated with resistance to Oxaliplatin as well as several chromatin cohesion protein that are relevant to CRC therapy. These data raise the prospect that CREB may have a role in GI malignancy as it does in other cancer types, but unlike Myb, is not critical for GI homeostasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mutations in multiple domains of c-Myb disrupt interaction with CBP/p300 and abrogate myeloid transforming ability.Mol Cancer Res. 2009 Sep;7(9):1477-86. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0070. Epub 2009 Sep 8. Mol Cancer Res. 2009. PMID: 19737967
-
HTLV-I Tax transrepresses the human c-Myb promoter independently of its interaction with CBP or p300.Oncogene. 2000 Apr 20;19(17):2155-64. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203536. Oncogene. 2000. PMID: 10815807
-
A transcription-factor-binding surface of coactivator p300 is required for haematopoiesis.Nature. 2002 Oct 17;419(6908):738-43. doi: 10.1038/nature01062. Nature. 2002. PMID: 12384703
-
CREB-binding protein, p300, butyrate, and Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Jul 21;21(27):8238-48. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i27.8238. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 26217075 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the PKA-regulated transcription factor CREB in development and tumorigenesis of endocrine tissues.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Jun;968:65-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04327.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002. PMID: 12119268 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of core genes for colorectal cancer prognosis based on immune and stromal scores.PeerJ. 2021 Nov 19;9:e12452. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12452. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34820188 Free PMC article.
-
Selective CREB-dependent cyclin expression mediated by the PI3K and MAPK pathways supports glioma cell proliferation.Oncogenesis. 2014 Jun 30;3(6):e108. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2014.21. Oncogenesis. 2014. PMID: 24979279 Free PMC article.
-
Cell signaling pathways involved in drug-mediated fetal hemoglobin induction: Strategies to treat sickle cell disease.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015 Aug;240(8):1050-64. doi: 10.1177/1535370215596859. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015. PMID: 26283707 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unleashing T cell anti-tumor immunity: new potential for 5-Nonloxytryptamine as an agent mediating MHC-I upregulation in tumors.Mol Cancer. 2023 Aug 15;22(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12943-023-01833-8. Mol Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37582744 Free PMC article.
-
CDK5 Inhibition Resolves PKA/cAMP-Independent Activation of CREB1 Signaling in Glioma Stem Cells.Cell Rep. 2018 May 8;23(6):1651-1664. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.04.016. Cell Rep. 2018. PMID: 29742423 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gregorieff A, Clevers H. Wnt signaling in the intestinal epithelium: from endoderm to cancer. Genes Dev. 2005;19:877–890. - PubMed
-
- Novak JM, Collins JT, Donowitz M, Farman J, Sheahan DG, Spiro HM. Effects of radiation on the human gastrointestinal tract. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1979;1:9–39. - PubMed
-
- Chang ML, Hou JK. Cancer risk related to gastrointestinal diagnostic radiation exposure. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. 2011;13:449–457. - PubMed
-
- Ishizuya-Oka A, Hasebe T. Sonic hedgehog and bone morphogenetic protein-4 signaling pathway involved in epithelial cell renewal along the radial axis of the intestine. Digestion. 2008;77 (Suppl 1:42–47. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

