Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) inhibits p53-dependent apoptosis through the collaboration with HDAC6 in response to DNA damage
- PMID: 23618908
- PMCID: PMC3641350
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2013.127
Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) inhibits p53-dependent apoptosis through the collaboration with HDAC6 in response to DNA damage
Abstract
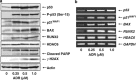
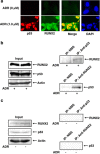
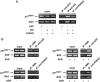
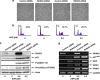
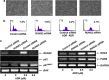
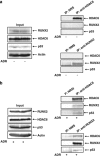
Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2) is the best known as an essential protein for osteoblast differentiation. In this study, we have found for the first time that RUNX2 acts as a negative regulator for p53 in response to DNA damage. On DNA damage mediated by adriamycin (ADR) exposure, p53 as well as RUNX2 was induced at protein and mRNA level in human osteosarcoma-derived U2OS cells in association with a significant upregulation of various p53-target genes. Indirect immunostaining and co-immunoprecipitation experiments demonstrated that RUNX2 colocalizes with p53 in cell nucleus and forms a complex with p53 following ADR treatment. Chromatin immunoprecipitation assays revealed that RUNX2/p53 complex is efficiently recruited onto p53-target promoters in response to ADR, suggesting that RUNX2 might be involved in the regulation of transcriptional activation mediated by p53. Indeed, forced expression of RUNX2 resulted in a remarkable downregulation of p53-target genes. Consistent with these observations, knockdown of RUNX2 enhanced ADR-mediated apoptosis and also elevated p53-target gene expression in response to ADR. On the other hand, depletion of RUNX2 in p53-deficient human lung carcinoma-derived H1299 cells had an undetectable effect on p53-target gene expression regardless of ADR treatment, indicating that RUNX2-mediated downregulation of p53-target genes is dependent on p53. Furthermore, RUNX2/p53 complex included histone deacetylase 6 (HDAC6) and HDAC6 was also recruited onto p53-target promoters following ADR exposure. Of note, HDAC6-specific chemical inhibitor tubacin treatment enhanced ADR-mediated upregulation of p53-target gene expression, indicating that deacetylase activity of HDAC6 is required for RUNX2-mediated downregulation of p53-target gene. Taken together, our present findings strongly suggest that RUNX2 inhibits DNA damage-induced transcriptional as well as pro-apoptotic activity of p53 through the functional collaboration with HDAC6 and therefore might be an attractive therapeutic target for cancer treatment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Runt-related transcription factor 2 attenuates the transcriptional activity as well as DNA damage-mediated induction of pro-apoptotic TAp73 to regulate chemosensitivity.FEBS J. 2015 Jan;282(1):114-28. doi: 10.1111/febs.13108. Epub 2014 Nov 10. FEBS J. 2015. PMID: 25331851 Free PMC article.
-
Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) stimulates tumor suppressor p53 protein in response to DNA damage through complex formation and acetylation.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 11;288(2):1353-64. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.402594. Epub 2012 Nov 12. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23148227 Free PMC article.
-
HDACs control RUNX2 expression in cancer cells through redundant and cell context-dependent mechanisms.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Aug 8;38(1):346. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1350-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31395086 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of RUNX2 on drug-resistant human pancreatic cancer cells with p53 mutations.BMC Cancer. 2018 Mar 20;18(1):309. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4217-9. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 29558908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Histone deacetylase co-repressor complex control of Runx2 and bone formation.Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2007;17(3):187-96. doi: 10.1615/critreveukargeneexpr.v17.i3.20. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr. 2007. PMID: 17725488 Review.
Cited by
-
Improvement of gemcitabine sensitivity of p53-mutated pancreatic cancer MiaPaCa-2 cells by RUNX2 depletion-mediated augmentation of TAp73-dependent cell death.Oncogenesis. 2016 Jun 13;5(6):e233. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2016.40. Oncogenesis. 2016. PMID: 27294865 Free PMC article.
-
Anoikis-resistant subpopulations of human osteosarcoma display significant chemoresistance and are sensitive to targeted epigenetic therapies predicted by expression profiling.J Transl Med. 2015 Apr 2;13:110. doi: 10.1186/s12967-015-0466-4. J Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 25889105 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear HDAC6 inhibits invasion by suppressing NF-κB/MMP2 and is inversely correlated with metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 6;6(30):30263-76. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4749. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26388610 Free PMC article.
-
Germline and somatic genetics of osteosarcoma - connecting aetiology, biology and therapy.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017 Aug;13(8):480-491. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2017.16. Epub 2017 Mar 24. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28338660 Review.
-
Selective Targeting of Class I Histone Deacetylases in a Model of Human Osteosarcoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 20;13(16):4199. doi: 10.3390/cancers13164199. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34439353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vousden KH, Lu X. Live or let die: the cell's response to p53. Nat Rev Cancer. 2002;2:594–604. - PubMed
-
- Oren M. Decision making by p53: life, death and cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2003;10:431–442. - PubMed
-
- Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991;253:49–53. - PubMed
-
- Harris CC. p53: at the crossroads of molecular carcinogenesis and risk assessment. Science. 1993;262:1980–1981. - PubMed
-
- Vogelstein B, Kinzler KW. p53 function and dysfunction. Cell. 1992;70:523–526. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

