Population genomics and transcriptional consequences of regulatory motif variation in globally diverse Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains
- PMID: 23619145
- PMCID: PMC3684857
- DOI: 10.1093/molbev/mst073
Population genomics and transcriptional consequences of regulatory motif variation in globally diverse Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains
Abstract
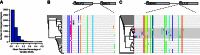
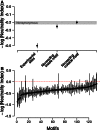
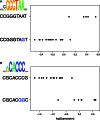
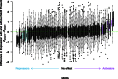
Noncoding genetic variation is known to significantly influence gene expression levels in a growing number of specific cases; however, the patterns of genome-wide noncoding variation present within populations, the evolutionary forces acting on noncoding variants, and the relative effects of regulatory polymorphisms on transcript abundance are not well characterized. Here, we address these questions by analyzing patterns of regulatory variation in motifs for 177 DNA binding proteins in 37 strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Between S. cerevisiae strains, we found considerable polymorphism in regulatory motifs across strains (mean π = 0.005) as well as diversity in regulatory motifs (mean 0.91 motifs differences per regulatory region). Population genetics analyses reveal that motifs are under purifying selection, and there is considerable heterogeneity in the magnitude of selection across different motifs. Finally, we obtained RNA-Seq data in 22 strains and identified 49 polymorphic DNA sequence motifs in 30 distinct genes that are significantly associated with transcriptional differences between strains. In 22 of these genes, there was a single polymorphic motif associated with expression in the upstream region. Our results provide comprehensive insights into the evolutionary trajectory of regulatory variation in yeast and the characteristics of a compendium of regulatory alleles.
Keywords: adaptive evolution; evolution; regulatory variation; yeast.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sequencing and comparison of yeast species to identify genes and regulatory elements.Nature. 2003 May 15;423(6937):241-54. doi: 10.1038/nature01644. Nature. 2003. PMID: 12748633
-
Personal and population genomics of human regulatory variation.Genome Res. 2012 Sep;22(9):1689-97. doi: 10.1101/gr.134890.111. Genome Res. 2012. PMID: 22955981 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution and selection in yeast promoters: analyzing the combined effect of diverse transcription factor binding sites.PLoS Comput Biol. 2008 Jan;4(1):e7. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.0040007. PLoS Comput Biol. 2008. PMID: 18193940 Free PMC article.
-
Ecological and evolutionary genomics of Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Ecol. 2006 Mar;15(3):575-91. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-294X.2006.02778.x. Mol Ecol. 2006. PMID: 16499686 Review.
-
Transcription factor-DNA binding: beyond binding site motifs.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017 Apr;43:110-119. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2017.02.007. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2017. PMID: 28359978 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The landscape of fitness effects of putatively functional noncoding mutations in humans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 14:2025.05.14.654124. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.14.654124. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40463122 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A deletion in the STA1 promoter determines maltotriose and starch utilization in STA1+ Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019 Sep;103(18):7597-7615. doi: 10.1007/s00253-019-10021-y. Epub 2019 Jul 26. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31346683 Free PMC article.
-
The molecular basis of phenotypic variation in yeast.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013 Dec;23(6):672-7. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2013.10.005. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2013. PMID: 24269094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell periphery-related proteins as major genomic targets behind the adaptive evolution of an industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain to combined heat and hydrolysate stress.BMC Genomics. 2015 Jul 9;16(1):514. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-1737-4. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26156140 Free PMC article.
-
Both Binding Strength and Evolutionary Accessibility Affect the Population Frequency of Transcription Factor Binding Sequences in Arabidopsis thaliana.Genome Biol Evol. 2021 Dec 1;13(12):evab273. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evab273. Genome Biol Evol. 2021. PMID: 34894231 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andolfatto P. Adaptive evolution of non-coding DNA in Drosophila. Nature. 2005;437:1149–1152. - PubMed
-
- Borneman AR, Gianoulis TA, Zhang ZD, Yu H, Rozowsky J, Seringhaus MR, Wang LY, Gerstein M, Snyder M. Divergence of transcription factor binding sites across related yeast species. Science. 2007;317:815–819. - PubMed
-
- Brem RB, Yvert G, Clinton R, Kruglyak L. Genetic dissection of transcriptional regulation in budding yeast. Science. 2002;296:752–755. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

