The absence of intrarenal ACE protects against hypertension
- PMID: 23619363
- PMCID: PMC3638907
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI65460
The absence of intrarenal ACE protects against hypertension
Abstract
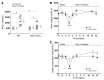
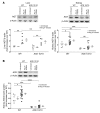
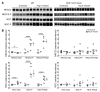
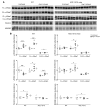
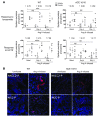
Activation of the intrarenal renin-angiotensin system (RAS) can elicit hypertension independently from the systemic RAS. However, the precise mechanisms by which intrarenal Ang II increases blood pressure have never been identified. To this end, we studied the responses of mice specifically lacking kidney angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) to experimental hypertension. Here, we show that the absence of kidney ACE substantially blunts the hypertension induced by Ang II infusion (a model of high serum Ang II) or by nitric oxide synthesis inhibition (a model of low serum Ang II). Moreover, the renal responses to high serum Ang II observed in wild-type mice, including intrarenal Ang II accumulation, sodium and water retention, and activation of ion transporters in the loop of Henle (NKCC2) and distal nephron (NCC, ENaC, and pendrin) as well as the transporter activating kinases SPAK and OSR1, were effectively prevented in mice that lack kidney ACE. These findings demonstrate that ACE metabolism plays a fundamental role in the responses of the kidney to hypertensive stimuli. In particular, renal ACE activity is required to increase local Ang II, to stimulate sodium transport in loop of Henle and the distal nephron, and to induce hypertension.
Figures


Comment in
-
Where hypertension happens.J Clin Invest. 2013 May;123(5):1934-6. doi: 10.1172/JCI69296. Epub 2013 Apr 24. J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23619355 Free PMC article.
-
Hypertension: Role of renal ACE in response to hypertensive stimuli.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013 Jul;9(7):372. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2013.97. Epub 2013 May 14. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2013. PMID: 23670086 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK083785/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK083785/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- HL088000/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103337/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL26371/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- GM074771/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK083785/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL110353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P20 RR017659/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20RR017659/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK083455/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R00 HL088000/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL026371/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 HL088000/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM074771/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R00DK083455/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL110353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

