Soluble polysialylated NCAM: a novel player of the innate immune system in the lung
- PMID: 23619613
- PMCID: PMC11113884
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-013-1342-0
Soluble polysialylated NCAM: a novel player of the innate immune system in the lung
Abstract
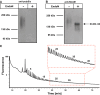
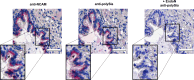
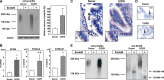
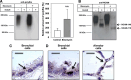
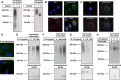
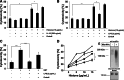
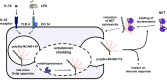
Posttranslational modification of the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) by polysialic acid (polySia) is well studied in the nervous system and described as a dynamic modulator of plastic processes like precursor cell migration, axon fasciculation, and synaptic plasticity. Here, we describe a novel function of polysialylated NCAM (polySia-NCAM) in innate immunity of the lung. In mature lung tissue of healthy donors, polySia was exclusively attached to the transmembrane isoform NCAM-140 and located to intracellular compartments of epithelial cells. In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, however, increased polySia levels and processing of the NCAM carrier were observed. Processing of polysialylated NCAM was reproduced in a mouse model by bleomycin administration leading to an activation of the inflammasome and secretion of interleukin (IL)-1β. As shown in a cell culture model, polySia-NCAM-140 was kept in the late trans-Golgi apparatus of lung epithelial cells and stimulation by IL-1β or lipopolysaccharide induced metalloprotease-mediated ectodomain shedding, resulting in the secretion of soluble polySia-NCAM. Interestingly, polySia chains of secreted NCAM neutralized the cytotoxic activity of extracellular histones as well as DNA/histone-network-containing "neutrophil extracellular traps", which are formed during invasion of microorganisms. Thus, shedding of polySia-NCAM by lung epithelial cells may provide a host-protective mechanism to reduce tissue damage during inflammatory processes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Regulation of extrasynaptic signaling by polysialylated NCAM: Impact for synaptic plasticity and cognitive functions.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017 Jun;81:12-21. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 27865768 Review.
-
Synaptic cell adhesion molecule SynCAM 1 is a target for polysialylation in postnatal mouse brain.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jun 1;107(22):10250-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912103107. Epub 2010 May 17. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 20479255 Free PMC article.
-
Polysialic acid on SynCAM 1 in NG2 cells and on neuropilin-2 in microglia is confined to intracellular pools that are rapidly depleted upon stimulation.Glia. 2015 Jul;63(7):1240-55. doi: 10.1002/glia.22815. Epub 2015 Mar 10. Glia. 2015. PMID: 25752299
-
Impact of the polysialyltransferases ST8SiaII and ST8SiaIV on polysialic acid synthesis during postnatal mouse brain development.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 18;283(3):1463-1471. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M708463200. Epub 2007 Nov 28. J Biol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18045870
-
Neuroimmunomodulatory properties of polysialic acid.Glycoconj J. 2023 Jun;40(3):277-294. doi: 10.1007/s10719-023-10120-z. Epub 2023 May 12. Glycoconj J. 2023. PMID: 37171513 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-throughput and high-efficiency sample preparation for single-cell proteomics using a nested nanowell chip.Nat Commun. 2021 Oct 29;12(1):6246. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26514-2. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34716329 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Distinct Populations of Carcinoma-Associated Fibroblasts from Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinoma Reveals a Role for ST8SIA2 in Cancer Cell Invasion.Neoplasia. 2019 May;21(5):482-493. doi: 10.1016/j.neo.2019.03.009. Epub 2019 Apr 9. Neoplasia. 2019. PMID: 30978569 Free PMC article.
-
Whole-genome expression analyses of type 2 diabetes in human skin reveal altered immune function and burden of infection.Oncotarget. 2017 May 23;8(21):34601-34609. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.16118. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28427244 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of neural cell adhesion molecule and polysialic acid in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016 Aug 15;7(1):113. doi: 10.1186/s13287-016-0373-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27528376 Free PMC article.
-
Polysialic Acid Modulates the Binding of External Lactoferrin in Neutrophil Extracellular Traps.Biology (Basel). 2019 Mar 28;8(2):20. doi: 10.3390/biology8020020. Biology (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30925725 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lackie PM, Zuber C, Roth J. Polysialic acid and N-CAM localisation in embryonic rat kidney: mesenchymal and epithelial elements show different patterns of expression. Development. 1990;110(3):933–947. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

