Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease
- PMID: 23619691
- PMCID: PMC3725458
- DOI: 10.1038/nature12034
Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease
Abstract
Macrophages, the most plastic cells of the haematopoietic system, are found in all tissues and show great functional diversity. They have roles in development, homeostasis, tissue repair and immunity. Although tissue macrophages are anatomically distinct from one another, and have different transcriptional profiles and functional capabilities, they are all required for the maintenance of homeostasis. However, these reparative and homeostatic functions can be subverted by chronic insults, resulting in a causal association of macrophages with disease states. In this Review, we discuss how macrophages regulate normal physiology and development, and provide several examples of their pathophysiological roles in disease. We define the 'hallmarks' of macrophages according to the states that they adopt during the performance of their various roles, taking into account new insights into the diversity of their lineages, identities and regulation. It is essential to understand this diversity because macrophages have emerged as important therapeutic targets in many human diseases.
Figures
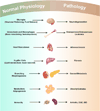

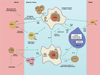
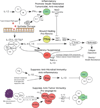
References
-
- Gordon S. Alternative activation of macrophages. Nat Rev Immunol. 2003;3:23–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- P01 CA100324/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1AR064158/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL076746/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK081405/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL076746/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 AR064158/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- DP1 OD006415/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P01CA100324/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK094641/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA131270/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA131270S/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- G1002033/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U54HD058155/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- DK094641/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

