Sprouts of RNA epigenetics: the discovery of mammalian RNA demethylases
- PMID: 23619745
- PMCID: PMC3904589
- DOI: 10.4161/rna.24711
Sprouts of RNA epigenetics: the discovery of mammalian RNA demethylases
Abstract
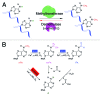
More than 100 structurally distinct RNA modifications have been identified in all kingdoms of life. These post-transcriptional modifications are widely present in various RNAs, including ribosomal RNA (rRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA), messenger RNA (mRNA), long non-coding RNA (lncRNA), etc. We have shown that the methylation of N(6)-methyladenine (m(6)A) can be reversed through the discovery of the first RNA demethylase, the human fat mass and obesity-associated protein, FTO, in 2011. (Most recently, we have identified a new mammalian RNA demethylase, ALKBH5, which is also able to remove the methyl group of m(6)A from RNA both in vitro and in vivo (Fig. 1A). The ALKBH5 protein colocalizes with nuclear speckles where pre-mRNA processing occurs. This protein is actively involved in mRNA export regulation, in which its demethylation activity seems to play an important role, as well as in RNA synthesis. A knockout of the Alkbh5 gene in mice resulted in impaired male fertility due to compromised spermatogenesis. Importantly, increased m(6)A levels were observed in mRNA isolated from the Alkbh5-knockout mouse organs compared to those from wild-type littermates. RNA-Seq results indicate aberrant gene expression in spermatogenic cells of the seminoferous tubulus of testes from Alkbh5-deficient mice, thereby showing that the loss of the m(6)A demethylase influences gene expression, which, in turn, leads to defects in spermatogenesis and increased apoptosis of meiotic cells. Thus, the discovery of FTO and this new RNA demethylase strongly suggests that the methylation of RNA, like DNA and histone modifications, is dynamically regulated and likely to play broad roles in mammalian cells.
Keywords: N6- methyladenine; RNA demethylase; RNA epigenetics; reversible RNA methylation.
Figures
Comment on
-
ALKBH5 is a mammalian RNA demethylase that impacts RNA metabolism and mouse fertility.Mol Cell. 2013 Jan 10;49(1):18-29. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.015. Epub 2012 Nov 21. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23177736 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources