Eradication of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms on cultured airway cells by a fosfomycin/tobramycin antibiotic combination
- PMID: 23620118
- PMCID: PMC4939271
- DOI: 10.1111/2049-632X.12015
Eradication of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms on cultured airway cells by a fosfomycin/tobramycin antibiotic combination
Abstract
Chronic biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis (CF) lungs is a major cause of morbidity and mortality for patients with CF. To gain insights into effectiveness of novel anti-infective therapies, the inhibitory effects of fosfomycin, tobramycin, and a 4:1 (wt/wt) fosfomycin/tobramycin combination (FTI) on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms grown on cultured human CF-derived airway cells (CFBE41o-) were investigated. In preformed biofilms treated for 16 h with antibiotics, P. aeruginosa CFU per mL were reduced 4 log10 units by both FTI and tobramycin at 256 mg L(-1) , while fosfomycin alone had no effect. Importantly, the FTI treatment contained five times less tobramycin than the tobramycin-alone treatment. Inhibition of initial biofilm formation was achieved at 64 mg L(-1) FTI and 16 mg L(-1) tobramycin. Fosfomycin (1024 mg L(-1)) did not inhibit biofilm formation. Cytotoxicity was also determined by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Intriguingly, sub-inhibitory concentrations of FTI (16 mg L(-1)) and tobramycin (4 mg L(-1)) and high concentrations of fosfomycin (1024 mg L(-1)) prevented bacterially mediated airway cell toxicity without a corresponding reduction in CFU. Overall, it was observed that FTI and tobramycin demonstrated comparable activity on biofilm formation and disruption. Decreased administration of tobramycin upon treatment with FTI might lead to a decrease in negative side effects of aminoglycosides.
© 2012 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
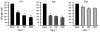
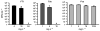

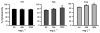
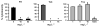
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

