Application of receiver operating characteristic analysis to refine the prediction of potential digoxin drug interactions
- PMID: 23620486
- PMCID: PMC3684818
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.112.050542
Application of receiver operating characteristic analysis to refine the prediction of potential digoxin drug interactions
Abstract
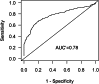
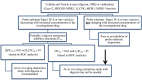
In the 2012 Food and Drug Administration (FDA) draft guidance on drug-drug interactions (DDIs), a new molecular entity that inhibits P-glycoprotein (P-gp) may need a clinical DDI study with a P-gp substrate such as digoxin when the maximum concentration of inhibitor at steady state divided by IC₅₀ ([I₁]/IC₅₀) is ≥0.1 or concentration of inhibitor based on highest approved dose dissolved in 250 ml divide by IC₅₀ ([I₂]/IC₅₀) is ≥10. In this article, refined criteria are presented, determined by receiver operating characteristic analysis, using IC₅₀ values generated by 23 laboratories. P-gp probe substrates were digoxin for polarized cell-lines and N-methyl quinidine or vinblastine for P-gp overexpressed vesicles. Inhibition of probe substrate transport was evaluated using 15 known P-gp inhibitors. Importantly, the criteria derived in this article take into account variability in IC₅₀ values. Moreover, they are statistically derived based on the highest degree of accuracy in predicting true positive and true negative digoxin DDI results. The refined criteria of [I₁]/IC₅₀ ≥ 0.03 and [I₂]/IC₅₀ ≥ 45 and FDA criteria were applied to a test set of 101 in vitro-in vivo digoxin DDI pairs collated from the literature. The number of false negatives (none predicted but DDI observed) were similar, 10 and 12%, whereas the number of false positives (DDI predicted but not observed) substantially decreased from 51 to 40%, relative to the FDA criteria. On the basis of estimated overall variability in IC₅₀ values, a theoretical 95% confidence interval calculation was developed for single laboratory IC₅₀ values, translating into a range of [I₁]/IC₅₀ and [I₂]/IC₅₀ values. The extent by which this range falls above the criteria is a measure of risk associated with the decision, attributable to variability in IC₅₀ values.
Figures
References
-
- Acharya P, O’Connor MP, Polli JW, Ayrton A, Ellens H, Bentz J. (2008) Kinetic identification of membrane transporters that assist P-glycoprotein-mediated transport of digoxin and loperamide through a confluent monolayer of MDCKII-hMDR1 cells. Drug Metab Dispos 36:452–460 - PubMed
-
- Agarwal S, Arya V, Zhang L. (2012) Review of P-gp inhibition data in recently approved new drug applications: utility of the proposed [I1]/IC50 and [I2]/IC50 criteria in the P-gp decision tree. J Clin Pharmacol, in press. - PubMed
-
- Anderle P, Niederer E, Rubas W, Hilgendorf C, Spahn-Langguth H, Wunderli-Allenspach H, Merkle HP, Langguth P. (1998) P-Glycoprotein (P-gp) mediated efflux in Caco-2 cell monolayers: the influence of culturing conditions and drug exposure on P-gp expression levels. J Pharm Sci 87:757–762 - PubMed
-
- Baris N, Kalkan S, Güneri S, Bozdemir V, Guven H. (2006) Influence of carvedilol on serum digoxin levels in heart failure: is there any gender difference? Eur J Clin Pharmacol 62:535–538 - PubMed
-
- Belz GG, Doering W, Munkes R, Matthews J. (1983) Interaction between digoxin and calcium antagonists and antiarrhythmic drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther 33:410–417 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous