Vascular lesions induced by renal nerve ablation as assessed by optical coherence tomography: pre- and post-procedural comparison with the Simplicity catheter system and the EnligHTN multi-electrode renal denervation catheter
- PMID: 23620498
- PMCID: PMC3717310
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht141
Vascular lesions induced by renal nerve ablation as assessed by optical coherence tomography: pre- and post-procedural comparison with the Simplicity catheter system and the EnligHTN multi-electrode renal denervation catheter
Abstract
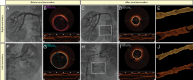
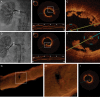
Aims: Catheter-based renal nerve ablation (RNA) using radiofrequency energy is a novel treatment for drug-resistant essential hypertension. However, the local endothelial and vascular injury induced by RNA has not been characterized, although this importantly determines the long-term safety of the procedure. Optical coherence tomography (OCT) enables in vivo visualization of morphologic features with a high resolution of 10-15 µm. The objective of this study was to assess the morphological features of the endothelial and vascular injury induced by RNA using OCT.
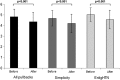
Methods and results: In a prospective observational study, 32 renal arteries of patients with treatment-resistant hypertension underwent OCT before and after RNA. All pre- and post-procedural OCT pullbacks were evaluated regarding vascular changes such as vasospasm, oedema (notches), dissection, and thrombus formation. Thirty-two renal arteries were evaluated, in which automatic pullbacks were obtained before and after RNA. Vasospasm was observed more often after RNA then before the procedure (0 vs. 42%, P < 0.001). A significant decrease in mean renal artery diameter after RNA was documented both with the EnligHTN (4.69 ± 0.73 vs. 4.21 ± 0.87 mm; P < 0.001) and with the Simplicity catheter (5.04 ± 0.66 vs. 4.57 ± 0.88 mm; P < 0.001). Endothelial-intimal oedema was noted in 96% of cases after RNA. The presence of thrombus formations was significantly higher after the RNA then before ablation (67 vs. 18%, P < 0.001). There was one evidence of arterial dissection after RNA with the Simplicity catheter, while endothelial and intimal disruptions were noted in two patients with the EnligHTN catheter.
Conclusion: Here we show that diffuse renal artery constriction and local tissue damage at the ablation site with oedema and thrombus formation occur after RNA and that OCT visualizes vascular lesions not apparent on angiography. This suggests that dual antiplatelet therapy may be required during RNA.
Keywords: Catheter-based renal nerve ablation; EnligHTN multi-electrode renal denervation catheter; Optical coherence tomography; Simplicity catheter system; Vascular lesions.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The safety of renal denervation as assessed by optical coherence tomography: pre- and post-procedure comparison with multi-electrode ablation catheter in animal experiment.Hellenic J Cardiol. 2020 May-Jun;61(3):190-196. doi: 10.1016/j.hjc.2019.01.009. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Hellenic J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 30684647
-
Safety and efficacy of a multi-electrode renal sympathetic denervation system in resistant hypertension: the EnligHTN I trial.Eur Heart J. 2013 Jul;34(28):2132-40. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht197. Epub 2013 Jun 19. Eur Heart J. 2013. PMID: 23782649 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term follow-up of renal arteries after radio-frequency catheter-based denervation using optical coherence tomography and angiography.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016 Jun;32(6):855-62. doi: 10.1007/s10554-016-0853-9. Epub 2016 Feb 16. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2016. PMID: 26883432
-
Review and meta-analysis of renal artery damage following percutaneous renal denervation with radiofrequency renal artery ablation.EuroIntervention. 2020 May 20;16(1):89-96. doi: 10.4244/EIJ-D-19-00902. EuroIntervention. 2020. PMID: 32038027 Review.
-
Pathophysiology of renal denervation procedures: from renal nerve anatomy to procedural parameters.EuroIntervention. 2013 May;9 Suppl R:R89-95. doi: 10.4244/EIJV9SRA15. EuroIntervention. 2013. PMID: 23732162 Review.
Cited by
-
Renal Denervation for Resistant Hypertension: Past, Present, and Future.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2015 Aug;17(8):65. doi: 10.1007/s11906-015-0577-6. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2015. PMID: 26134635 Review.
-
Renal denervation: intractable hypertension and beyond.Cardiorenal Med. 2014 Apr;4(1):22-33. doi: 10.1159/000357597. Epub 2014 Jan 15. Cardiorenal Med. 2014. PMID: 24847331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Device-based Therapy for Hypertension.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016 Aug;18(8):61. doi: 10.1007/s11906-016-0670-5. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016. PMID: 27370788 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Renal Denervation for Treatment of Hypertension: a Second Start and New Challenges.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016 Jan;18(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s11906-015-0610-9. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2016. PMID: 26739586 Review.
-
Seeing is believing - Imaging of a plaque in the renal artery.J Cardiol Cases. 2013 Dec 13;9(2):84-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jccase.2013.09.011. eCollection 2014 Feb. J Cardiol Cases. 2013. PMID: 30534303 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Kearney PM, Whelton M, Reynolds K, Muntner P, Whelton PK, He J. Global burden of hypertension: analysis of worldwide data. Lancet. 2005;365:217–223. - PubMed
-
- Turnbull F, Neal B, Ninomiya T, Algert C, Arima H, Barzi F, Bulpitt C, Chalmers J, Fagard R, Gleason A, Heritier S, Li N, Perkovic V, Woodward M, MacMahon S. Effects of different regimens to lower blood pressure on major cardiovascular events in older and younger adults: meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ. 2008;336:1121–1123. doi:10.1136/bmj.39548.738368.BE. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet. 2002;360:1903–1913. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11911-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lawes CM, Vander Hoorn S, Rodgers A. Global burden of blood-pressure-related disease, 2001. Lancet. 2008;371:1513–1518. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(08)60655-8. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mancia G, Laurent S, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Burnier M, Caulfield MJ, Cifkova R, Clement D, Coca A, Dominiczak A, Erdine S, Fagard R, Farsang C, Grassi G, Haller H, Heagerty A, Kjeldsen SE, Kiowski W, Mallion JM, Manolis A, Narkiewicz K, Nilsson P, Olsen MH, Rahn KH, Redon J, Rodicio J, Ruilope L, Schmieder RE, Struijker-Boudier HA, van Zwieten PA, Viigimaa M, Zanchetti A. Reappraisal of European guidelines on hypertension management: a European Society of Hypertension Task Force document. J Hypertens. 2009;27:2121–2158. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e328333146d. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

