Durable tumor regression in genetically altered malignant rhabdoid tumors by inhibition of methyltransferase EZH2
- PMID: 23620515
- PMCID: PMC3651445
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1303800110
Durable tumor regression in genetically altered malignant rhabdoid tumors by inhibition of methyltransferase EZH2
Abstract
Inactivation of the switch/sucrose nonfermentable complex component SMARCB1 is extremely prevalent in pediatric malignant rhabdoid tumors (MRTs) or atypical teratoid rhabdoid tumors. This alteration is hypothesized to confer oncogenic dependency on EZH2 in these cancers. We report the discovery of a potent, selective, and orally bioavailable small-molecule inhibitor of EZH2 enzymatic activity, (N-((4,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)methyl)-5-(ethyl(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)amino)-4-methyl-4'-(morpholinomethyl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-carboxamide). The compound induces apoptosis and differentiation specifically in SMARCB1-deleted MRT cells. Treatment of xenograft-bearing mice with (N-((4,6-dimethyl-2-oxo-1,2-dihydropyridin-3-yl)methyl)-5-(ethyl(tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-yl)amino)-4-methyl-4'-(morpholinomethyl)-[1,1'-biphenyl]-3-carboxamide) leads to dose-dependent regression of MRTs with correlative diminution of intratumoral trimethylation levels of lysine 27 on histone H3, and prevention of tumor regrowth after dosing cessation. These data demonstrate the dependency of SMARCB1 mutant MRTs on EZH2 enzymatic activity and portend the utility of EZH2-targeted drugs for the treatment of these genetically defined cancers.
Keywords: EZH2 inhibitor; epigenetic cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: All authors except V.M.R. are employees of Epizyme, Inc.
Figures

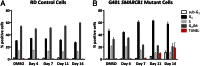
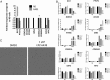

References
-
- Richon VM, et al. Chemogenetic analysis of human protein methyltransferases. Chem Biol Drug Des. 2011;78(2):199–210. - PubMed
-
- Chase A, Cross NC. Aberrations of EZH2 in cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(9):2613–2618. - PubMed
-
- Knutson SK, et al. A selective inhibitor of EZH2 blocks H3K27 methylation and kills mutant lymphoma cells. Nat Chem Biol. 2012;8(11):890–896. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

