Misplaced helix slows down ultrafast pressure-jump protein folding
- PMID: 23620522
- PMCID: PMC3657825
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1219163110
Misplaced helix slows down ultrafast pressure-jump protein folding
Abstract
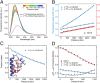
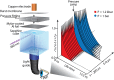
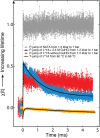
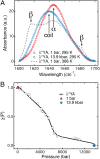
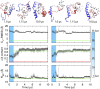
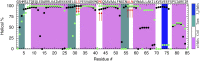
Using a newly developed microsecond pressure-jump apparatus, we monitor the refolding kinetics of the helix-stabilized five-helix bundle protein λ*YA, the Y22W/Q33Y/G46,48A mutant of λ-repressor fragment 6-85, from 3 μs to 5 ms after a 1,200-bar P-drop. In addition to a microsecond phase, we observe a slower 1.4-ms phase during refolding to the native state. Unlike temperature denaturation, pressure denaturation produces a highly reversible helix-coil-rich state. This difference highlights the importance of the denatured initial condition in folding experiments and leads us to assign a compact nonnative helical trap as the reason for slower P-jump-induced refolding. To complement the experiments, we performed over 50 μs of all-atom molecular dynamics P-drop refolding simulations with four different force fields. Two of the force fields yield compact nonnative states with misplaced α-helix content within a few microseconds of the P-drop. Our overall conclusion from experiment and simulation is that the pressure-denatured state of λ*YA contains mainly residual helix and little β-sheet; following a fast P-drop, at least some λ*YA forms misplaced helical structure within microseconds. We hypothesize that nonnative helix at helix-turn interfaces traps the protein in compact nonnative conformations. These traps delay the folding of at least some of the population for 1.4 ms en route to the native state. Based on molecular dynamics, we predict specific mutations at the helix-turn interfaces that should speed up refolding from the pressure-denatured state, if this hypothesis is correct.
Keywords: downhill folding; fluorescence lifetime; lambda repressor; molecular dynamics simulation; thermal denaturation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sarupria S, Ghosh T, García AE, Garde S. Studying pressure denaturation of a protein by molecular dynamics simulations. Proteins. 2010;78(7):1641–1651. - PubMed
-
- Callender R, Dyer RB. Probing protein dynamics using temperature jump relaxation spectroscopy. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2002;12(5):628–633. - PubMed
-
- Clegg RM, Elson EL, Maxfield BW. New technique for optical observation of the kinetics of chemical reactions perturbed by small pressure changes. Biopolymers. 1975;14(4):883–887.
-
- Schiewek M, Krumova M, Hempel G, Blume A. Pressure jump relaxation setup with IR detection and millisecond time resolution. Rev Sci Instrum. 2007;78(4):045101. - PubMed
-
- Dumont C, Emilsson T, Gruebele M. Reaching the protein folding speed limit with large, sub-microsecond pressure jumps. Nat Methods. 2009;6(7):515–519. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

