Risk assessment and genetic counseling in families with Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 23620649
- PMCID: PMC3631803
Risk assessment and genetic counseling in families with Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Abstract
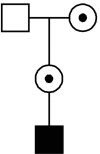
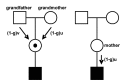
The Duchenne Muscular dystrophy (DMD) is the most frequent muscle disorder in childhood caused by mutations in the Xlinked dystrophin gene (about 65% deletions, about 7% duplications, about 26% point mutations and about 2% unknown mutations). The clinically milder Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD) is allelic to DMD. About 33% of all patients are due to de novo mutations and germ line mosaicism is frequently observed. While in earlier studies equal mutation rates in males and females had been reported, a breakdown by mutation types can better explain the sex ratio of mutations: Point mutations and duplications arise preferentially during spermatogenesis whereas deletions mostly arise in oogenesis. With current analytical methods, the underlying mutation can be identified in the great majority of cases and be used for carrier detection. However, in families with no mutation carrier available, the genetic model to be used for counselling of relatives can be quite complex.
Keywords: Becker muscular dystrophy; Duchenne muscular dystrophy; dystrophin gene; genetic model; germ line mosaicism; molecular genetic diagnosis.
Figures


References
-
- Emery AE. Population frequencies of inherited neuromuscular diseases--a world survey. Neuromuscul Disord. 1991;1:19–29. - PubMed
-
- White SJ, Aartsma-Rus A, Flanigan KM, et al. Duplications in the DMD gene. Hum Mutat. 2006;27:938–945. - PubMed
-
- Deburgrave N, Daoud F, Llense S, et al. Protein- and mRNA-based phenotype-genotype correlations in DMD/BMD with point mutations and molecular basis for BMD with nonsense and frameshift mutations in the DMD gene. Hum Mutat. 2007;28:183–195. - PubMed
-
- Lalic T, Vossen RH, Coffa J, et al. Deletion and duplication screening in the DMD gene using MLPA. Eur J Hum Genet. 2005;13:1231–1234. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
