Characterization and comparative profiling of MicroRNAs in a sexual dimorphism insect, Eupolyphaga sinensis Walker
- PMID: 23620723
- PMCID: PMC3631196
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059016
Characterization and comparative profiling of MicroRNAs in a sexual dimorphism insect, Eupolyphaga sinensis Walker
Abstract
Background: MicroRNAs are now recognized as key post-transcriptional regulators in animal ontogenesis and phenotypic diversity. Eupolyphaga sinensis Walker (Blattaria) is a sexually dimorphic insect, which is also an important source of material used in traditional Chinese medicine. The male E. sinensis have shorter lifecycles and go through fewer instars than the female. Furthermore, the males have forewings, while the females are totally wingless.
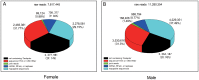
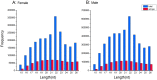
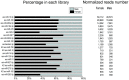
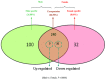
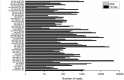
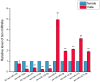
Results: We used the Illumina/Solexa deep sequencing technology to sequence small RNA libraries prepared from the fourth-instar larvae of male and female E. sinensis. 19,097,799 raw reads were yielded in total: 7,817,445 reads from the female library and 11,280,354 from the male, respectively. As a result, we identified 168 known miRNAs belonging to 55 families as well as 204 novel miRNAs. Moreover, 45 miRNAs showed significantly different expression between the female and the male fourth-instar larvae, and we validated 10 of them by Stem-loop qRT-PCR. Some of these differentially expressed miRNAs are related to metamorphosis, development and phenotypic diversity.
Conclusions/significance: This is the first comprehensive description of miRNAs in E. sinensis. The results provide a useful resource for further in-depth study on molecular regulation and evolution of miRNAs. These findings not only enrich miRNAs for hemimetabolans but also lay the foundation for the study of post-transcriptional regulation on the phenomena of sexual dimorphism.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Identification and characterization of microRNAs from Chinese pollination constant non-astringent persimmon using high-throughput sequencing.BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Jan 21;15:11. doi: 10.1186/s12870-014-0400-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 25604351 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of microRNAs in mud crab Scylla paramamosain under Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection.PLoS One. 2013 Aug 30;8(8):e73392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0073392. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24023678 Free PMC article.
-
Deep sequencing of organ- and stage-specific microRNAs in the evolutionarily basal insect Blattella germanica (L.) (Dictyoptera, Blattellidae).PLoS One. 2011 Apr 28;6(4):e19350. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0019350. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21552535 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs of the mesothorax in Qinlingacris elaeodes, an alpine grasshopper showing a wing polymorphism with unilateral wing form.Bull Entomol Res. 2016 Apr;106(2):225-32. doi: 10.1017/S0007485315000991. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Bull Entomol Res. 2016. PMID: 26693589
-
Scoping review of the medicinal effects of Eupolyphaga sinensis Walker and the underlying mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Oct 5;296:115454. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115454. Epub 2022 Jun 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35700853
Cited by
-
Accuracy of microRNA discovery pipelines in non-model organisms using closely related species genomes.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 3;9(1):e84747. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084747. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24404190 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs of Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus 1762) conserved in six orders of the class Insecta.Sci Rep. 2021 May 21;11(1):10706. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90095-9. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34021209 Free PMC article.
-
Sex-Biased Gene Expression of Mesobuthus martensii Collected from Gansu Province, China, Reveals Their Different Therapeutic Potentials.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Aug 19;2021:1967158. doi: 10.1155/2021/1967158. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34462639 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs of two medically important mosquito species: Aedes aegypti and Anopheles stephensi.Insect Mol Biol. 2015 Apr;24(2):240-52. doi: 10.1111/imb.12152. Epub 2014 Nov 24. Insect Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 25420875 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Novel and Conserved microRNAs in Homalodisca vitripennis, the Glassy-Winged Sharpshooter by Expression Profiling.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 6;10(10):e0139771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139771. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26440407 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116: 281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V (2004) The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature 431: 350–355. - PubMed
-
- Miska EA (2005) How microRNAs control cell division, differentiation and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev 15: 563–568. - PubMed
-
- Wienholds E, Plasterk RH (2005) MicroRNA function in animal development. FEBS Lett 579: 5911–5922. - PubMed
-
- Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kinoshita T, Okamoto Y, Seki N (2012) MicroRNAs function as tumor suppressors or oncogenes: Aberrant expression of microRNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

