The evidence for association of ATP2B2 polymorphisms with autism in Chinese Han population
- PMID: 23620727
- PMCID: PMC3631200
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061021
The evidence for association of ATP2B2 polymorphisms with autism in Chinese Han population
Abstract
Background: Autism is a neurodevelopmental disorder with a high estimated heritability. ATP2B2, located on human chromosome 3p25.3, encodes the plasma membrane calcium-transporting ATPase 2 which extrudes Ca(2+) from cytosol into extracellular space. Recent studies reported association between ATP2B2 and autism in samples from Autism Genetic Resource Exchange (AGRE) and Italy. In this study, we investigated whether ATP2B2 polymorphisms were associated with autism in Chinese Han population.
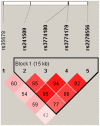
Methods: We performed a family based association study between five SNPs (rs35678 in exon, rs241509, rs3774180, rs3774179, and rs2278556 in introns) in ATP2B2 and autism in 427 autism trios of Han Chinese descent. All SNPs were genotyped using the Sequenom genotyping platform. The family-based association test (FBAT) program was used to perform association test for SNPs and haplotype analyses.
Results: This study demonstrated a preferential transmission of T allele of rs3774179 to affected offsprings under an additive model (T>C, Z = 2.482, p = 0.013). While C allele of rs3774179 showed an undertransmission from parents to affected children under an additive and a dominant model, respectively (Z = -2.482, p = 0.013; Z = -2.591, p = 0.0096). Haplotype analyses revealed that three haplotypes were significantly associated with autism. The haplotype C-C (rs3774180-rs3774179) showed a significant undertransmission from parents to affected offsprings both in specific and global haplotype FBAT (Z = -2.037, p = 0.042; Global p = 0.03). As for the haplotype constructed by rs3774179 and rs2278556, C-A might be a protective haplotype (Z = -2.206, p = 0.027; Global p = 0.04), while T-A demonstrated an excess transmission from parents to affected offsprings (Z = 2.143, p = 0.032). These results were still significant after using the permutation method to obtain empirical p values.
Conclusions: Our research suggested that ATP2B2 might play a role in the etiology of autism in Chinese Han population.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Converging evidence for an association of ATP2B2 allelic variants with autism in male subjects.Biol Psychiatry. 2011 Nov 1;70(9):880-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.05.020. Epub 2011 Jul 14. Biol Psychiatry. 2011. PMID: 21757185
-
Evidence for association between Disrupted-in-Schizophrenia 1 (DISC1) gene polymorphisms and autism in Chinese Han population: a family-based association study.Behav Brain Funct. 2011 May 15;7:14. doi: 10.1186/1744-9081-7-14. Behav Brain Funct. 2011. PMID: 21569632 Free PMC article.
-
Schizophrenia Related Variants in CACNA1C also Confer Risk of Autism.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 23;10(7):e0133247. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133247. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26204268 Free PMC article.
-
Association analysis of CNTNAP2 polymorphisms with autism in the Chinese Han population.Psychiatr Genet. 2010 Jun;20(3):113-7. doi: 10.1097/YPG.0b013e32833a216f. Psychiatr Genet. 2010. PMID: 20414140
-
Positive association of the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR) with autism in the Chinese Han population.Biol Psychiatry. 2005 Jul 1;58(1):74-7. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.03.013. Biol Psychiatry. 2005. PMID: 15992526
Cited by
-
ADNP is essential for sex-dependent hippocampal neurogenesis, through male unfolded protein response and female mitochondrial gene regulation.Mol Psychiatry. 2025 Jun;30(6):2696-2706. doi: 10.1038/s41380-024-02879-w. Epub 2024 Dec 23. Mol Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39715923 Free PMC article.
-
Research and Discussion on the Relationships between Noise-Induced Hearing Loss and ATP2B2 Gene Polymorphism.Int J Genomics. 2019 Dec 1;2019:5048943. doi: 10.1155/2019/5048943. eCollection 2019. Int J Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31886164 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for a role of plasma membrane calcium pumps in neurodegenerative disease: Recent developments.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Jan 10;663:39-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2017.08.035. Epub 2017 Aug 19. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 28827127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of neurons from immortalized dental pulp stem cells for the study of neurogenetic disorders.Stem Cell Res. 2015 Nov;15(3):722-730. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2015.11.004. Epub 2015 Dec 1. Stem Cell Res. 2015. PMID: 26599327 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic profiling reveals gene expression in human peripheral blood after exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation.J Radiat Res. 2022 Jan 20;63(1):8-18. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrab091. J Radiat Res. 2022. PMID: 34788452 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association, Washington DC (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, Fourth Edition.
-
- Fombonne E (2005) Epidemiology of autistic disorder and other pervasive developmental disorders. J Clin Psychiatry 66 Suppl 103–8. - PubMed
-
- Folstein S, Rutter M (1977) Infantile autism: a genetic study of 21 twin pairs. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 18: 297–321. - PubMed
-
- Steffenburg S, Gillberg C, Hellgren L, Andersson L, Gillberg IC, et al. (1989) A twin study of autism in Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 30: 405–416. - PubMed
-
- Bailey A, Le Couteur A, Gottesman I, Bolton P, Simonoff E, et al. (1995) Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: evidence from a British twin study. Psychol Med 25: 63–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

