The index-based subgraph matching algorithm (ISMA): fast subgraph enumeration in large networks using optimized search trees
- PMID: 23620730
- PMCID: PMC3631255
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061183
The index-based subgraph matching algorithm (ISMA): fast subgraph enumeration in large networks using optimized search trees
Abstract
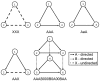
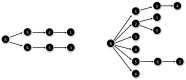
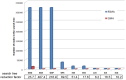
Subgraph matching algorithms are designed to find all instances of predefined subgraphs in a large graph or network and play an important role in the discovery and analysis of so-called network motifs, subgraph patterns which occur more often than expected by chance. We present the index-based subgraph matching algorithm (ISMA), a novel tree-based algorithm. ISMA realizes a speedup compared to existing algorithms by carefully selecting the order in which the nodes of a query subgraph are investigated. In order to achieve this, we developed a number of data structures and maximally exploited symmetry characteristics of the subgraph. We compared ISMA to a naive recursive tree-based algorithm and to a number of well-known subgraph matching algorithms. Our algorithm outperforms the other algorithms, especially on large networks and with large query subgraphs. An implementation of ISMA in Java is freely available at http://sourceforge.net/projects/isma/.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
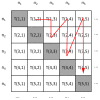
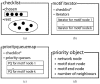
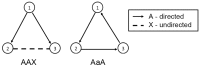
 from node 1 to node 2, a directed link of type
from node 1 to node 2, a directed link of type  from node 1 to node 3, a directed link of type
from node 1 to node 3, a directed link of type  from node 2 to node 3, a directed link of type
from node 2 to node 3, a directed link of type  from node 1 to node 4, no link between node 2 and node 4, no link between node 3 and node 4, no link between node 1 and node 5, a directed link of type
from node 1 to node 4, no link between node 2 and node 4, no link between node 3 and node 4, no link between node 1 and node 5, a directed link of type  from node 2 to node 5, no link between node 3 and node 5, a directed link of type
from node 2 to node 5, no link between node 3 and node 5, a directed link of type  from node 4 to node 5, no link between node 1 and node 6, no link between node 2 and node 6, a directed link of type
from node 4 to node 5, no link between node 1 and node 6, no link between node 2 and node 6, a directed link of type  from node 3 to node 6, a directed link of type
from node 3 to node 6, a directed link of type  from node 4 to node 6, a directed link of type
from node 4 to node 6, a directed link of type  from node 5 to node 6.
from node 5 to node 6.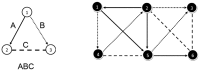



Similar articles
-
The Index-based Subgraph Matching Algorithm with General Symmetries (ISMAGS): exploiting symmetry for faster subgraph enumeration.PLoS One. 2014 May 30;9(5):e97896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097896. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24879305 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient sampling algorithm for estimating subgraph concentrations and detecting network motifs.Bioinformatics. 2004 Jul 22;20(11):1746-58. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bth163. Epub 2004 Mar 4. Bioinformatics. 2004. PMID: 15001476
-
A linear delay algorithm for enumerating all connected induced subgraphs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2019 Jun 20;20(Suppl 12):319. doi: 10.1186/s12859-019-2837-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2019. PMID: 31216984 Free PMC article.
-
Network subgraph-based approach for analyzing and comparing molecular networks.PeerJ. 2022 May 3;10:e13137. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13137. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35529499 Free PMC article.
-
Grasping frequent subgraph mining for bioinformatics applications.BioData Min. 2018 Sep 3;11:20. doi: 10.1186/s13040-018-0181-9. eCollection 2018. BioData Min. 2018. PMID: 30202444 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Generating random graphs with prescribed graphlet frequency bounds derived from probabilistic networks.PLoS One. 2025 Aug 26;20(8):e0328639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0328639. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40857227 Free PMC article.
-
An Algorithm to Automatically Generate the Combinatorial Orbit Counting Equations.PLoS One. 2016 Jan 21;11(1):e0147078. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0147078. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26797021 Free PMC article.
-
Edge-colored directed subgraph enumeration on the connectome.Sci Rep. 2022 Jul 5;12(1):11349. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-15027-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35790766 Free PMC article.
-
Function, dynamics and evolution of network motif modules in integrated gene regulatory networks of worm and plant.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jul 27;46(13):6480-6503. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky468. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29873777 Free PMC article.
-
The Index-based Subgraph Matching Algorithm with General Symmetries (ISMAGS): exploiting symmetry for faster subgraph enumeration.PLoS One. 2014 May 30;9(5):e97896. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097896. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24879305 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jasny B, Zahn L, Marshall E (2009) Connections. Science (New York, NY) 325: 405. - PubMed
-
- Milo R, Shen-Orr S, Itzkovitz S, Kashtan N, Chklovskii D, et al. (2002) Network motifs: simple building blocks of complex networks. Science 298: 824–827. - PubMed
-
- Alon U (2007) Network motifs: theory and experimental approaches. Nat Rev Genet 8: 450–461. - PubMed
-
- Kashtan N, Itzkovitz S, Milo R, Alon U (2004) Topological generalizations of network motifs. Phys Rev E 70: 031909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

