CADM1 is a key receptor mediating human mast cell adhesion to human lung fibroblasts and airway smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 23620770
- PMCID: PMC3631237
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061579
CADM1 is a key receptor mediating human mast cell adhesion to human lung fibroblasts and airway smooth muscle cells
Abstract
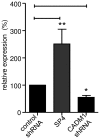
Background: Mast cells (MCs) play a central role in the development of many diseases including asthma and pulmonary fibrosis. Interactions of human lung mast cells (HLMCs) with human airway smooth muscle cells (HASMCs) are partially dependent on adhesion mediated by cell adhesion molecule-1 (CADM1), but the adhesion mechanism through which HLMCs interact with human lung fibroblasts (HLFs) is not known. CADM1 is expressed as several isoforms (SP4, SP1, SP6) in HLMCs, with SP4 dominant. These isoforms differentially regulate HLMC homotypic adhesion and survival.
Objective: In this study we have investigated the role of CADM1 isoforms in the adhesion of HLMCs and HMC-1 cells to primary HASMCs and HLFs.
Methods: CADM1 overexpression or downregulation was achieved using adenoviral delivery of CADM1 short hairpin RNAs or isoform-specific cDNAs respectively.
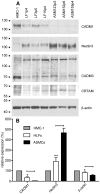
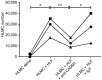
Results: Downregulation of CADM1 attenuated both HLMC and HMC-1 adhesion to both primary HASMCs and HLFs. Overexpression of either SP1 or SP4 isoforms did not alter MC adhesion to HASMCs, whereas overexpression of SP4, but not SP1, significantly increased both HMC-1 cell and HLMC adhesion to HLFs. The expression level of CADM1 SP4 strongly predicted the extent of MC adhesion; linear regression indicated that CADM1 accounts for up to 67% and 32% of adhesion to HLFs for HMC-1 cells and HLMCs, respectively. HLFs supported HLMC proliferation and survival through a CADM1-dependent mechanism. With respect to CADM1 counter-receptor expression, HLFs expressed both CADM1 and nectin-3, whereas HASMCs expressed only nectin-3.
Conclusion and clinical relevance: Collectively these data indicate that the CADM1 SP4 isoform is a key receptor mediating human MC adhesion to HASMCs and HLFs. The differential expression of CADM1 counter-receptors on HLFs compared to HASMCs may allow the specific targeting of either HLMC-HLF or HLMC-HASMC interactions in the lung parenchyma and airways.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
CADM1 isoforms differentially regulate human mast cell survival and homotypic adhesion.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012 Aug;69(16):2751-64. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-0948-y. Epub 2012 Mar 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2012. PMID: 22438059 Free PMC article.
-
CADM1 is expressed as multiple alternatively spliced functional and dysfunctional isoforms in human mast cells.Mol Immunol. 2013 Apr;53(4):345-54. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2012.08.024. Epub 2012 Oct 11. Mol Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23063768 Free PMC article.
-
Bidirectional Counterregulation of Human Lung Mast Cell and Airway Smooth Muscle β2 Adrenoceptors.J Immunol. 2016 Jan 1;196(1):55-63. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1402232. Epub 2015 Nov 25. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26608913 Free PMC article.
-
Nerve-mast cell and smooth muscle-mast cell interaction mediated by cell adhesion molecule-1, CADM1.J Smooth Muscle Res. 2008 Apr;44(2):83-93. doi: 10.1540/jsmr.44.83. J Smooth Muscle Res. 2008. PMID: 18552455 Review.
-
Multiple Functions of Cell Adhesion Molecule 1 (CADM1) and Its Role in the Pathogenesis of Cancer and Other Diseases.J Nippon Med Sch. 2025;92(2):122-131. doi: 10.1272/jnms.JNMS.2025_92-205. J Nippon Med Sch. 2025. PMID: 40399107 Review.
Cited by
-
The Use of Kosher Phenotyping for Mapping QTL Affecting Susceptibility to Bovine Respiratory Disease.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 14;11(4):e0153423. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0153423. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27077383 Free PMC article.
-
Role of mechanoregulation in mast cell-mediated immune inflammation of the smooth muscle in the pathophysiology of esophageal motility disorders.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024 Apr 1;326(4):G398-G410. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00258.2023. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38290993 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Expression of CADM1 in Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors of Different Sites and with Different Gene Abnormalities.Pathol Oncol Res. 2021 Apr 19;27:602008. doi: 10.3389/pore.2021.602008. eCollection 2021. Pathol Oncol Res. 2021. PMID: 34257559 Free PMC article.
-
Mast Cells and Sensory Nerves Contribute to Neurogenic Inflammation and Pruritus in Chronic Skin Inflammation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2019 Sep 18;13:422. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00422. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31619965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mast cell-mediated and associated disorders in pregnancy: a risky game with an uncertain outcome?Front Immunol. 2014 May 19;5:231. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00231. eCollection 2014. Front Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24904581 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Moiseeva EP, Bradding P (2011) Mast cells in lung inflammation. Adv Exp Med Biol 716: 235–269. - PubMed
-
- Heard BE, Dewar A, Corrin B (1992) Apposition of fibroblasts to mast cells and lymphocytes in normal human lung and in cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Ultrastructure and cell perimeter measurements. J Pathol 166: 303–310. - PubMed
-
- Pesci A, Bertorelli G, Gabrielli M, Olivieri D (1993) Mast cells in fibrotic lung disorders. Chest 103: 989–996. - PubMed
-
- Bradding P, Roberts JA, Britten KM, Montefort S, Djukanovic R, et al. (1994) Interleukin-4, -5, and -6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in normal and asthmatic airways: evidence for the human mast cell as a source of these cytokines. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 10: 471–480. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

