Hepatitis B virus X protein up-regulates tumor necrosis factor-α expression in cultured mesangial cells via ERKs and NF-κB pathways
- PMID: 23620841
- PMCID: PMC3631753
- DOI: 10.1016/S2221-1691(13)60053-2
Hepatitis B virus X protein up-regulates tumor necrosis factor-α expression in cultured mesangial cells via ERKs and NF-κB pathways
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of hepatitis B virus (HBV) X protein (HBx) on the expression of tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in glomerular mesangial cells (GMCs) and the underlying intracellular signal pathways.
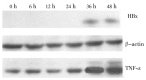
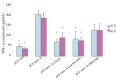
Methods: The plasmid pCI-neo-X that carries the X gene of hepatitis B virus was transfected into cultured GMCs. HBx expression in the transfected GMCs was assessed by Western-blot. TNF-α protein and mRNA were assessed by ELISA and semi-quantitative RT-PCR, respectively. Three kinase inhibitors-U0126, an inhibitor of extracellular signal-regulated kinases (ERKs); lactacystin, an inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB); and SB203580, a selective inhibitor of p38 MAP kinase (p38 MAPK) were used to determine which intracellular signal pathways may underlie the action of HBx on TNF-α expression in transfected GMCs.
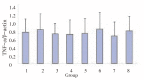
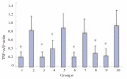
Results: A significant increase in HBx expression in pCI-neo-X transfected GMCs was detected at 36 h and 48 h, which was not affected by any of those kinase inhibitors mentioned above. A similar increase in the expression of both TNF-α protein and mRNA was also observed at 36 h and 48 h, which was significantly decreased in the presence of U0126 or lactacytin, but not SB203580.
Conclusions: HBx upregulates TNF-α expression in cultured GMCs, possibly through ERKs and NF-κB pathway, but not p38 MAPK pathway.
Keywords: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase; Glomerulonephritis; Heptitis B virus; Nuclear factor-κB; Tumor necrosis factor-α; X protein.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatitis B viral HBx induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression through activation of ERK and PI-3K/AKT pathways: involvement of invasive potential.FASEB J. 2004 Jul;18(10):1123-5. doi: 10.1096/fj.03-1429fje. Epub 2004 May 7. FASEB J. 2004. PMID: 15132991
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α regulates matrix metalloproteinase-2 expression and cell migration via ERK pathway in rat glomerular mesangial cells.Cell Biol Int. 2014 Sep;38(9):1060-8. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10298. Epub 2014 May 13. Cell Biol Int. 2014. PMID: 24802761
-
Additive activation of hepatic NF-kappaB by ethanol and hepatitis B protein X (HBX) or HCV core protein: involvement of TNF-alpha receptor 1-independent and -dependent mechanisms.FASEB J. 2001 Nov;15(13):2551-3. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0217. Epub 2001 Sep 17. FASEB J. 2001. PMID: 11641261
-
Lipoxin A4 inhibits TNF-alpha-induced production of interleukins and proliferation of rat mesangial cells.Kidney Int. 2005 Jul;68(1):35-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00379.x. Kidney Int. 2005. PMID: 15954894
-
Hepatitis B virus, HBx mutants and their role in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 14;20(30):10238-48. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10238. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25132741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Suppression of Interferon-α Treatment Response by Host Negative Factors in Hepatitis B Virus Infection.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Nov 24;8:784172. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.784172. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34901094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus X protein decreases nephrin expression and induces podocyte apoptosis via activating STAT3.Exp Ther Med. 2019 May;17(5):4223-4229. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7453. Epub 2019 Mar 29. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 31007753 Free PMC article.
-
The tripartite leader sequence is required for ectopic expression of HAdV-B and HAdV-E E3 CR1 genes.Virology. 2017 May;505:139-147. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2017.02.021. Epub 2017 Mar 1. Virology. 2017. PMID: 28259047 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of HBx Protein in Diseases Beyond the Liver.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 May 23;16:3225-3232. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S405316. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37249958 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Shi C, Huang J, Liu X, Zeng X, Cheng C, Yin Q, et al. et al. Diagnostic significance of hepatitis B viral antigens in patients with glomerulonephritis-associated hepatitis B virus infection. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. 2012;72(2):156–160. - PubMed
-
- Xu G, Huang T. Hepatitis B virus-associated glomerular nephritis in East Asia: progress and challenges. Eur J Int Med. 2011;22(2):161–166. - PubMed
-
- Mesquit M, Lasser L, Langlet P. Long-term (7-years) treatment with lamivdine monotherapy in HBV-associated glomerulonephritis. Clin Nephrol. 2008;70(1):69–71. - PubMed
-
- Yi Z, Jie YW, Nan Z. The efficacy of anti-viral therapy on hepatitis B virus-associated glomerulonephritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Hepatol. 2011;10(2):165–173. - PubMed
-
- Sakallioglu O, Gok F, Kalman S, Kurekci AE, Gunhan O, Gokcay E. Hepatitis B complicated focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. J Nephrol. 2005;18(4):433–435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

