Transfusion of murine red blood cells expressing the human KEL glycoprotein induces clinically significant alloantibodies
- PMID: 23621760
- PMCID: PMC3732531
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.12217
Transfusion of murine red blood cells expressing the human KEL glycoprotein induces clinically significant alloantibodies
Abstract
Background: Red blood cell (RBC) alloantibodies to nonself antigens may develop after transfusion or pregnancy, leading to morbidity and mortality in the form of hemolytic transfusion reactions or hemolytic disease of the newborn. A better understanding of the mechanisms of RBC alloantibody induction, or strategies to mitigate the consequences of such antibodies, may ultimately improve transfusion safety. However, such studies are inherently difficult in humans.
Study design and methods: We recently generated transgenic mice with RBC-specific expression of the human KEL glycoprotein, specifically the KEL2 or KEL1 antigens. Herein, we investigate recipient alloimmune responses to transfused RBCs in this system.
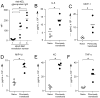
Results: Transfusion of RBCs from KEL2 donors into wild-type recipients (lacking the human KEL protein but expressing the murine KEL ortholog) resulted in dose-dependent anti-KEL glycoprotein immunoglobulin (Ig)M and IgG antibody responses, enhanced by recipient inflammation with poly(I:C). Boostable responses were evident upon repeat transfusion, with morbid-appearing alloimmunized recipients experiencing rapid clearance of transfused KEL2 but not control RBCs. Although KEL1 RBCs were also immunogenic after transfusion into wild-type recipients, transfusion of KEL1 RBCs into KEL2 recipients or vice versa failed to lead to detectable anti-KEL1 or anti-KEL2 responses.
Conclusions: This murine model, with reproducible and clinically significant KEL glycoprotein alloantibody responses, provides a platform for future mechanistic studies of RBC alloantibody induction and consequences. Long-term translational goals of these studies include improving transfusion safety for at-risk patients.
© 2013 American Association of Blood Banks.
Figures

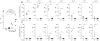



References
-
- FDA. Fatalities Reported to the FDA Following Blood Collection. 2012 http://wwwfdagov/BiologicsBloodVaccines/SafetyAvailability.
-
- Moise KJ, Jr, Argoti PS. Management and prevention of red cell alloimmunization in pregnancy: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120(5):1132–1139. - PubMed
-
- Reid ME, Mohandas N. Red blood cell blood group antigens: structure and function. Seminars in Hematology. 2004;41(2):93–117. - PubMed
-
- Reid ME, Lomas-Francis C. The Blood Group Antigen Facts Book. 2. Amsterdam: Elsevier Academic Press; 2004.
-
- Brinc D, Denomme GA, Lazarus AH. Mechanisms of anti-D action in the prevention of hemolytic disease of the fetus and newborn: what can we learn from rodent models? Curr Opin Hematol. 2009;16(6):488–496. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

