Marine collagen scaffolds for nasal cartilage repair: prevention of nasal septal perforations in a new orthotopic rat model using tissue engineering techniques
- PMID: 23621795
- PMCID: PMC3762606
- DOI: 10.1089/ten.TEA.2012.0650
Marine collagen scaffolds for nasal cartilage repair: prevention of nasal septal perforations in a new orthotopic rat model using tissue engineering techniques
Abstract
Autologous grafts are frequently needed for nasal septum reconstruction. Because they are only available in limited amounts, there is a need for new cartilage replacement strategies. Tissue engineering based on the use of autologous chondrocytes and resorbable matrices might be a suitable option. So far, an optimal material for nasal septum reconstruction has not been identified. The aim of our study was to provide the first evaluation of marine collagen for use in nasal cartilage repair. First, we studied the suitability of marine collagen as a cartilage replacement matrix in the context of in vitro three dimensional cultures by analyzing cell migration, cytotoxicity, and extracellular matrix formation using human and rat nasal septal chondrocytes. Second, we worked toward developing a suitable orthotopic animal model for nasal septum repair, while simultaneously evaluating the biocompatibility of marine collagen. Seeded and unseeded scaffolds were transplanted into nasal septum defects in an orthotopic rat model for 1, 4, and 12 weeks. Explanted scaffolds were histologically and immunohistochemically evaluated. Scaffolds did not induce any cytotoxic reactions in vitro. Chondrocytes were able to adhere to marine collagen and produce cartilaginous matrix proteins, such as collagen type II. Treating septal cartilage defects in vivo with seeded and unseeded scaffolds led to a significant reduction in the number of nasal septum perforations compared to no replacement. In summary, we demonstrated that marine collagen matrices provide excellent properties for cartilage tissue engineering. Marine collagen scaffolds are able to prevent septal perforations in an autologous, orthotopic rat model. This newly described experimental surgical procedure is a suitable way to evaluate new scaffold materials for their applicability in the context of nasal cartilage repair.
Figures
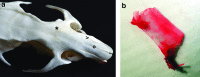

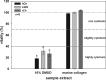
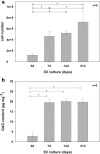
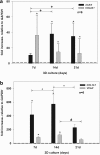
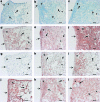
 cell nuclei. Color images available online at
cell nuclei. Color images available online at 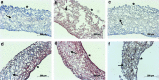
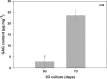
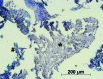

References
-
- Rotter N. Haisch A. Bucheler M. Cartilage and bone tissue engineering for reconstructive head and neck surgery. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2005;262:539. - PubMed
-
- Mandl E.W. Jahr H. Koevoet J.L. van Leeuwen J.P. Weinans H. Verhaar J.A. Van Osch G.J. Fibroblast growth factor-2 in serum-free medium is a potent mitogen and reduces dedifferentiation of human ear chondrocytes in monolayer culture. Matrix Biol. 2004;23:231. - PubMed
-
- Rotter N. Bucheler M. Haisch A. Wollenberg B. Lang S. Cartilage tissue engineering using resorbable scaffolds. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2007;1:411. - PubMed
-
- Nagata S. Modification of the stages in total reconstruction of the auricle: Part I. Grafting the three-dimensional costal cartilage framework for lobule-type microtia. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;93:221. - PubMed
-
- Ohara K. Nakamura K. Ohta E. Chest wall deformities and thoracic scoliosis after costal cartilage graft harvesting. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1997;99:1030. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

