Associative learning enhances population coding by inverting interneuronal correlation patterns
- PMID: 23622067
- PMCID: PMC3641681
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.02.023
Associative learning enhances population coding by inverting interneuronal correlation patterns
Abstract
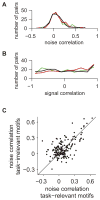
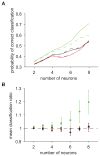
Learning-dependent cortical encoding has been well described in single neurons. But behaviorally relevant sensory signals drive the coordinated activity of millions of cortical neurons; whether learning produces stimulus-specific changes in population codes is unknown. Because the pattern of firing rate correlations between neurons--an emergent property of neural populations--can significantly impact encoding fidelity, we hypothesize that it is a target for learning. Using an associative learning procedure, we manipulated the behavioral relevance of natural acoustic signals and examined the evoked spiking activity in auditory cortical neurons in songbirds. We show that learning produces stimulus-specific changes in the pattern of interneuronal correlations that enhance the ability of neural populations to recognize signals relevant for behavior. This learning-dependent enhancement increases with population size. The results identify the pattern of interneuronal correlation in neural populations as a target of learning that can selectively enhance the representations of specific sensory signals.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures





Comment in
-
Population code, noise correlations, and memory.Neuron. 2013 Apr 24;78(2):209-10. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.04.012. Neuron. 2013. PMID: 23622058 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Song recognition learning and stimulus-specific weakening of neural responses in the avian auditory forebrain.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Apr;103(4):1785-97. doi: 10.1152/jn.00885.2009. Epub 2010 Jan 27. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20107117 Free PMC article.
-
Perceptual learning directs auditory cortical map reorganization through top-down influences.J Neurosci. 2006 May 3;26(18):4970-82. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3771-05.2006. J Neurosci. 2006. PMID: 16672673 Free PMC article.
-
Spike Train Coactivity Encodes Learned Natural Stimulus Invariances in Songbird Auditory Cortex.J Neurosci. 2021 Jan 6;41(1):73-88. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0248-20.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 11. J Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33177068 Free PMC article.
-
Neural coding strategies in auditory cortex.Hear Res. 2007 Jul;229(1-2):81-93. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2007.01.019. Epub 2007 Jan 25. Hear Res. 2007. PMID: 17346911 Review.
-
Learning-induced plasticity in animal and human auditory cortex.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005 Aug;15(4):470-7. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2005.07.002. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2005. PMID: 16009546 Review.
Cited by
-
A Redundant Cortical Code for Speech Envelope.J Neurosci. 2023 Jan 4;43(1):93-112. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1616-21.2022. Epub 2022 Nov 15. J Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36379706 Free PMC article.
-
Task engagement selectively modulates neural correlations in primary auditory cortex.J Neurosci. 2015 May 13;35(19):7565-74. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4094-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25972181 Free PMC article.
-
Triplet correlations among similarly tuned cells impact population coding.Front Comput Neurosci. 2015 May 18;9:57. doi: 10.3389/fncom.2015.00057. eCollection 2015. Front Comput Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26042024 Free PMC article.
-
The development of cortical circuits for motion discrimination.Nat Neurosci. 2015 Feb;18(2):252-61. doi: 10.1038/nn.3921. Epub 2015 Jan 19. Nat Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25599224 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal variability in orbitofrontal cortex during economic decisions.J Neurophysiol. 2015 Sep;114(3):1367-81. doi: 10.1152/jn.00231.2015. Epub 2015 Jun 17. J Neurophysiol. 2015. PMID: 26084903 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbott LF, Dayan P. The effect of correlated variability on the accuracy of a population code. Neural Computation. 1999;11:91–101. - PubMed
-
- Averbeck BB, Latham PE, Pouget A. Neural correlations, population coding and computation. Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 2006;7:358–366. - PubMed
-
- Bartho P, Hirase H, Monconduit L, Zugaro M, Harris KD, Buzsaki G. Characterization of neocortical principal cells and interneurons by network interactions and extracellular features. Journal of neurophysiology. 2004;92:600–608. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

