Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1, 3-dihydroxyxanthone mannich base derivatives as anticholinesterase agents
- PMID: 23622085
- PMCID: PMC3673835
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-153X-7-78
Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1, 3-dihydroxyxanthone mannich base derivatives as anticholinesterase agents
Abstract
Background: Alzheimer's disease (AD), a progressive and degenerative disorder, has become one of the severe problems among the aged population all over the world. To use cholinesterase inhibitor drugs has become the most predominant treatment strategy for AD.
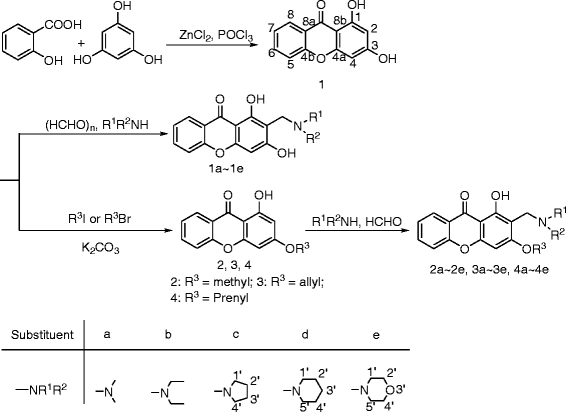
Results: A series of novel 1, 3-dihydroxyxanthone Mannich bases derivatives (1a ~ 4e) were synthesized, structure elucidated and evaluated for anti-cholinesterase activity. The result showed that most of the target compounds exhibited moderate to good inhibitory activities with the IC50 values at micromole level concentration against both acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE). The preliminary structure-activity indicated that: (i) The alkoxy or alkenoxy substituents in the position 3 of xanthone have a positive influence on the inhibition potency; (ii) types of dialkylamine methyl in position 2 of xanthone affected cholinesterase activities and AChE/BuChE selectivity. Among them, 2-((diethylamino)methyl)-1-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyloxy)-9H-xanthen-9-one showed potent inhibitory activity against AChE with the IC50 value of 2.61 ± 0.13 μM and the best inhibitory activity against BuChE with the IC50 value of 0.51 ± 0.01 μM. The results of a mixed-type manner in enzyme kinetic experiment and molecular docking study for 2-((diethylamino)methyl)-1-hydroxy-3-(3-methylbut-2-enyloxy)-9H-xanthen-9-one demonstrated that the Mannich base derivatives were likely to bind to the active site (AS) and the peripheral anionic site (PAS) of cholinesterases.
Conclusions: This study suggested that 1, 3-dihydroxyxanthone Mannich base derivatives were potential dual inhibitors of both AChE and BuChE, which may be considered as a kind of novel drug candidates for treatment of AD.
Figures
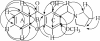
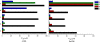
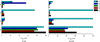
Similar articles
-
Design, Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Xanthone Derivatives for Possible Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease Based on Multi-Target Strategy.Chem Biodivers. 2020 Oct;17(10):e2000442. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202000442. Epub 2020 Sep 21. Chem Biodivers. 2020. PMID: 32692899
-
Design, synthesis and biological activity of novel tacrine-isatin Schiff base hybrid derivatives.Bioorg Chem. 2019 Aug;89:103006. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2019.103006. Epub 2019 May 21. Bioorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31158577
-
Discovery of potent and selective acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitors: acacetin 7-O-methyl ether Mannich base derivatives synthesised from easy access natural product naringin.Nat Prod Res. 2018 Mar;32(6):743-747. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2017.1340280. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Nat Prod Res. 2018. PMID: 28617100
-
Design, synthesis and preliminary structure-activity relationship investigation of nitrogen-containing chalcone derivatives as acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors: a further study based on Flavokawain B Mannich base derivatives.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016 Aug;31(4):580-9. doi: 10.3109/14756366.2015.1050009. Epub 2015 Jul 17. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26186269
-
An overview on the synthesis of carbohydrate-based molecules with biological activity related to neurodegenerative diseases.RSC Med Chem. 2021 Sep 8;12(12):2001-2015. doi: 10.1039/d1md00217a. eCollection 2021 Dec 15. RSC Med Chem. 2021. PMID: 35028560 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Xanthones: Biosynthesis and Trafficking in Plants, Fungi and Lichens.Plants (Basel). 2023 Feb 4;12(4):694. doi: 10.3390/plants12040694. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36840041 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mannich bases in medicinal chemistry and drug design.Eur J Med Chem. 2015 Jan 7;89:743-816. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2014.10.076. Epub 2014 Oct 30. Eur J Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 25462280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview of structure-based activity outcomes of pyran derivatives against Alzheimer's disease.Saudi Pharm J. 2023 Jun;31(6):998-1018. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2023.04.030. Epub 2023 May 8. Saudi Pharm J. 2023. PMID: 37234350 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shoot cultures of Hoppea fastigiata (Griseb.) C.B. Clarke as potential source of neuroprotective xanthones.J Nat Med. 2015 Jul;69(3):375-86. doi: 10.1007/s11418-015-0904-x. Epub 2015 Apr 22. J Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25900046
-
Cytotoxic and Enzyme Inhibitory Potential of Two Potentilla species (P. speciosa L. and P. reptans Willd.) and Their Chemical Composition.Front Pharmacol. 2017 May 23;8:290. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00290. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28588492 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

