Inflammation, autophagy, and obesity: common features in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 23622129
- PMCID: PMC3786712
- DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.007
Inflammation, autophagy, and obesity: common features in the pathogenesis of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer
Abstract
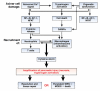
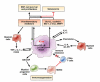
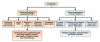
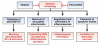
Inflammation and autophagy are cellular defense mechanisms. When these processes are deregulated (deficient or overactivated) they produce pathologic effects, such as oxidative stress, metabolic impairments, and cell death. Unresolved inflammation and disrupted regulation of autophagy are common features of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Furthermore, obesity, a risk factor for pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer, promotes inflammation and inhibits or deregulates autophagy, creating an environment that facilitates the induction and progression of pancreatic diseases. However, little is known about how inflammation, autophagy, and obesity interact to promote exocrine pancreatic disorders. We review the roles of inflammation and autophagy, and their deregulation by obesity, in pancreatic diseases. We discuss the connections among disordered pathways and important areas for future research.
Copyright © 2013 AGA Institute. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Mantovani A, Cassatella MA, Costantini C, et al. Neutrophils in the activation and regulation of innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:519–531. - PubMed
-
- Nathan C, Ding A. Nonresolving inflammation. Cell. 2010;140:871–882. - PubMed
-
- Soehnlein O, Lindbom L. Phagocyte partnership during the onset and resolution of inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2010;10:427–439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- AI043477/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- AA19730/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AI043477/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DK59936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- CA163798/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA163200/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03CA167120/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA019730/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK059936/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AA011999/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA163798/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R03 CA167120/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI043477/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

