MicroRNAs inhibit the translation of target mRNAs on the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis
- PMID: 23622241
- PMCID: PMC3694718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.005
MicroRNAs inhibit the translation of target mRNAs on the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis
Abstract
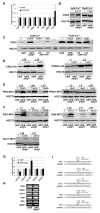
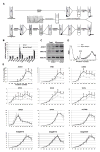
Translation inhibition is a major but poorly understood mode of action of microRNAs (miRNAs) in plants and animals. In particular, the subcellular location where this process takes place is unknown. Here, we show that the translation inhibition, but not the mRNA cleavage activity, of Arabidopsis miRNAs requires ALTERED MERISTEM PROGRAM1 (AMP1). AMP1 encodes an integral membrane protein associated with endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and ARGONAUTE1, the miRNA effector and a peripheral ER membrane protein. Large differences in polysome association of miRNA target RNAs are found between wild-type and the amp1 mutant for membrane-bound, but not total, polysomes. This, together with AMP1-independent recruitment of miRNA target transcripts to membrane fractions, shows that miRNAs inhibit the translation of target RNAs on the ER. This study demonstrates that translation inhibition is an important activity of plant miRNAs, reveals the subcellular location of this activity, and uncovers a previously unknown function of the ER.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




Comment in
-
MicroRNAs visit the ER.Cell. 2013 Apr 25;153(3):511-2. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.014. Cell. 2013. PMID: 23622236
Similar articles
-
Cytoplasmic HYL1 modulates miRNA-mediated translational repression.Plant Cell. 2021 Jul 19;33(6):1980-1996. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab090. Plant Cell. 2021. PMID: 33764452 Free PMC article.
-
ALTERED MERISTEM PROGRAM1 Restricts Shoot Meristem Proliferation and Regeneration by Limiting HD-ZIP III-Mediated Expression of RAP2.6L.Plant Physiol. 2018 Aug;177(4):1580-1594. doi: 10.1104/pp.18.00252. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Plant Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29884678 Free PMC article.
-
Trip to ER: MicroRNA-mediated translational repression in plants.RNA Biol. 2013 Oct;10(10):1586-92. doi: 10.4161/rna.26313. Epub 2013 Sep 10. RNA Biol. 2013. PMID: 24100209 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs, mRNAs, and translation.Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006;71:531-5. doi: 10.1101/sqb.2006.71.043. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 2006. PMID: 17381336 Review.
-
Argonautes compete for miR165/166 to regulate shoot apical meristem development.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2012 Dec;15(6):652-8. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2012.05.007. Epub 2012 Jun 21. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2012. PMID: 22727764 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TarDB: an online database for plant miRNA targets and miRNA-triggered phased siRNAs.BMC Genomics. 2021 May 13;22(1):348. doi: 10.1186/s12864-021-07680-5. BMC Genomics. 2021. PMID: 33985427 Free PMC article.
-
Absence of Polyphenol Oxidase in Cynomorium coccineum, a Widespread Holoparasitic Plant.Plants (Basel). 2020 Jul 30;9(8):964. doi: 10.3390/plants9080964. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32751574 Free PMC article.
-
The Small Molecule Hyperphyllin Enhances Leaf Formation Rate and Mimics Shoot Meristem Integrity Defects Associated with AMP1 Deficiency.Plant Physiol. 2016 Jun;171(2):1277-90. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01633. Epub 2016 May 3. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27208298 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular RNA: mechanisms of secretion and potential functions.J Exp Bot. 2023 Apr 9;74(7):2389-2404. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac512. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 36609873 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated mRNA and miRNA Transcriptome Analysis Suggests a Regulatory Network for UV-B-Controlled Terpenoid Synthesis in Fragrant Woodfern (Dryopteris fragrans).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 May 20;23(10):5708. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105708. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35628519 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birckbichler PJ, Pryme IF. Fractionation of membrane-bound polysomes, free polysomes, and nuclei from tissue-cultured cells. Eur J Biochem. 1978;33:368–373. - PubMed
-
- Brodersen P, Sakvarelidze-Achard L, Bruun-Rasmussen M, Dunoyer P, Yamamoto YY, Sieburth L, Voinnet O. Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science. 2008;320:1185–1190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

