Integrated systems approach identifies genetic nodes and networks in late-onset Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 23622250
- PMCID: PMC3677161
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.030
Integrated systems approach identifies genetic nodes and networks in late-onset Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
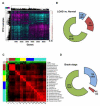
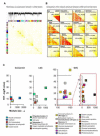
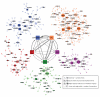
The genetics of complex disease produce alterations in the molecular interactions of cellular pathways whose collective effect may become clear through the organized structure of molecular networks. To characterize molecular systems associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD), we constructed gene-regulatory networks in 1,647 postmortem brain tissues from LOAD patients and nondemented subjects, and we demonstrate that LOAD reconfigures specific portions of the molecular interaction structure. Through an integrative network-based approach, we rank-ordered these network structures for relevance to LOAD pathology, highlighting an immune- and microglia-specific module that is dominated by genes involved in pathogen phagocytosis, contains TYROBP as a key regulator, and is upregulated in LOAD. Mouse microglia cells overexpressing intact or truncated TYROBP revealed expression changes that significantly overlapped the human brain TYROBP network. Thus the causal network structure is a useful predictor of response to gene perturbations and presents a framework to test models of disease mechanisms underlying LOAD.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Bertram L, Lill CM, Tanzi RE. The genetics of Alzheimer disease: back to the future. Neuron. 2010;68:270–281. - PubMed
-
- Bettens K, Sleegers K, Van Broeckhoven C. Genetic insights in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:92–104. - PubMed
-
- Bianchin MM, Martin KC, de Souza AC, de Oliveira MA, Rieder CR. Nasu-Hakola disease and primary microglial dysfunction. Nat Rev Neurol. 2010;6:193–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 AG17917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG030146/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG10161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG034504/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS032765/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG011101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- K08 AG034290/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS032765/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG15819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG11101/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

