Antiproliferative activity of 2,3-disubstituted indoles toward apoptosis-resistant cancers cells
- PMID: 23622980
- PMCID: PMC3915534
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.03.110
Antiproliferative activity of 2,3-disubstituted indoles toward apoptosis-resistant cancers cells
Abstract
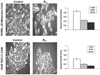
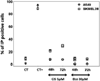
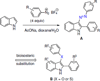
Many types of cancer, including glioma, melanoma, NSCLC, among others, are resistant to apoptosis induction and poorly responsive to current therapies with propaptotic agents. We describe a series of 2,3-disubstituted indoles, which display cytostatic rather than cytotoxic effects in cancer cells, and serve as a new chemical scaffold to develop anticancer agents capable of combating apoptosis-resistant cancers associated with dismal prognoses.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
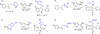
References
-
- Brenner H. The Lancet. 2002;360:1131. - PubMed
-
- Kleihues P, Cavenee WK. Pathology and Genetics of Tumors of the Nervous System, International Agency for the Research on Cancer (IARC) and WHO Health Organization. Oxford, UK: Oxford Press; 2000.
-
- Lefranc F, Sadeghi N, Camby I, Metens T, De Witte O, Kiss R. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2006;6:719. - PubMed
-
- Stupp R, Hegi ME, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Taphoorn MJ, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Allgeier A, Fisher B, Belanger K, et al. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459. - PubMed
-
- Giese A, Bjerkvig R, Berens ME, Westphal M. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003;21:1624. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

