Semantic processes leading to true and false memory formation in schizophrenia
- PMID: 23623175
- PMCID: PMC3679292
- DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2013.04.007
Semantic processes leading to true and false memory formation in schizophrenia
Abstract
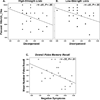
Encoding semantic relationships between items on word lists (semantic processing) enhances true memories, but also increases memory distortions. Episodic memory impairments in schizophrenia (SZ) are strongly driven by failures to process semantic relations, but the exact nature of these relational semantic processing deficits is not well understood. Here, we used a false memory paradigm to investigate the impact of implicit and explicit semantic processing manipulations on episodic memory in SZ. Thirty SZ and 30 demographically matched healthy controls (HC) studied Deese/Roediger-McDermott (DRM) lists of semantically associated words. Half of the lists had strong implicit semantic associations and the remainder had low strength associations. Similarly, half of the lists were presented under "standard" instructions and the other half under explicit "relational processing" instructions. After study, participants performed recall and old/new recognition tests composed of targets, critical lures, and unrelated lures. HC exhibited higher true memories and better discriminability between true and false memory compared to SZ. High, versus low, associative strength increased false memory rates in both groups. However, explicit "relational processing" instructions positively improved true memory rates only in HC. Finally, true and false memory rates were associated with severity of disorganized and negative symptoms in SZ. These results suggest that reduced processing of semantic relationships during encoding in SZ may stem from an inability to implement explicit relational processing strategies rather than a fundamental deficit in the implicit activation and retrieval of word meanings from patients' semantic lexicon.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Figures
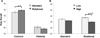
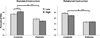
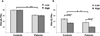
Similar articles
-
False Memories in Individuals With Stabilized Schizophrenia.Psychol Rep. 2023 Oct;126(5):2119-2140. doi: 10.1177/00332941221083213. Epub 2022 Apr 4. Psychol Rep. 2023. PMID: 35379032 Review.
-
False memory and schizophrenia: evidence for gist memory impairment.Psychol Med. 2007 Apr;37(4):559-67. doi: 10.1017/S0033291706009044. Epub 2006 Nov 1. Psychol Med. 2007. PMID: 17076913
-
Towards a genetics of semantics? False memories and semantic memory organization in Williams syndrome.Neuropsychologia. 2025 Apr 15;210:109106. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2025.109106. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Neuropsychologia. 2025. PMID: 40024325
-
From vector spaces to DRM lists: False Memory Generator, a software for automated generation of lists of stimuli inducing false memories.Behav Res Methods. 2024 Apr;56(4):3779-3793. doi: 10.3758/s13428-024-02425-0. Epub 2024 May 6. Behav Res Methods. 2024. PMID: 38710986 Free PMC article.
-
[Schizophrenia and semantic priming effects].Encephale. 2006 Jan-Feb;32(1 Pt 1):75-82. doi: 10.1016/s0013-7006(06)76139-5. Encephale. 2006. PMID: 16633293 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Differential patterns of contextual organization of memory in first-episode psychosis.NPJ Schizophr. 2018 Feb 15;4(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41537-018-0046-8. NPJ Schizophr. 2018. PMID: 29449557 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired Self-Monitoring of Inner Speech in Schizophrenia Patients with Verbal Hallucinations and in Non-clinical Individuals Prone to Hallucinations.Front Psychol. 2016 Sep 14;7:1381. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01381. eCollection 2016. Front Psychol. 2016. PMID: 27683568 Free PMC article.
-
Memory deficit in patients with schizophrenia and posttraumatic stress disorder: relational vs item-specific memory.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016 May 10;12:1157-66. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S104384. eCollection 2016. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2016. PMID: 27274250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retrieval practice improves memory in patients with schizophrenia: new perspectives for cognitive remediation.BMC Psychiatry. 2019 Nov 11;19(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s12888-019-2341-y. BMC Psychiatry. 2019. PMID: 31711448 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Investigating False Memory and Illusory Pattern Perception Bias in Schizophrenia Patients with and without Delusions.Cognit Ther Res. 2023 May 26:1-12. doi: 10.1007/s10608-023-10393-6. Online ahead of print. Cognit Ther Res. 2023. PMID: 37363747 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barch DM, Servan-Schreiber D, Steingard S, Cohen JD, Steinhauer SS, Van Kammen DP. Semantic priming in schizophrenia: an examination of spreading activation using word pronunciation and multiple SOAs. J. Abnorm. Psychology. 1996;105:592–601. - PubMed
-
- Brainerd CJ, Reyna VF, Ceci SJ. Developmental reversals in false memory: a review of data and theory. Psychol. Bull. 2008;134:343–382. - PubMed
-
- Brebion G, David AS, Jones H, Pilowsky LS. Semantic organization and verbal memory efficiency in patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychology. 2004;18:378–383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

