Pathogenesis of growth failure and partial reversal with gene therapy in murine and canine Glycogen Storage Disease type Ia
- PMID: 23623482
- PMCID: PMC3764490
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2013.03.018
Pathogenesis of growth failure and partial reversal with gene therapy in murine and canine Glycogen Storage Disease type Ia
Abstract
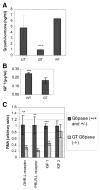
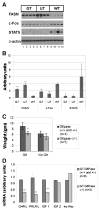
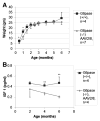
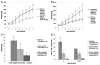
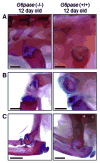
Glycogen Storage Disease type Ia (GSD-Ia) in humans frequently causes delayed bone maturation, decrease in final adult height, and decreased growth velocity. This study evaluates the pathogenesis of growth failure and the effect of gene therapy on growth in GSD-Ia affected dogs and mice. Here we found that homozygous G6pase (-/-) mice with GSD-Ia have normal growth hormone (GH) levels in response to hypoglycemia, decreased insulin-like growth factor (IGF) 1 levels, and attenuated weight gain following administration of GH. Expression of hepatic GH receptor and IGF 1 mRNAs and hepatic STAT5 (phospho Y694) protein levels are reduced prior to and after GH administration, indicating GH resistance. However, restoration of G6Pase expression in the liver by treatment with adeno-associated virus 8 pseudotyped vector expressing G6Pase (AAV2/8-G6Pase) corrected body weight, but failed to normalize plasma IGF 1 in G6pase (-/-) mice. Untreated G6pase (-/-) mice also demonstrated severe delay of growth plate ossification at 12 days of age; those treated with AAV2/8-G6Pase at 14 days of age demonstrated skeletal dysplasia and limb shortening when analyzed radiographically at 6 months of age, in spite of apparent metabolic correction. Moreover, gene therapy with AAV2/9-G6Pase only partially corrected growth in GSD-Ia affected dogs as detected by weight and bone measurements and serum IGF 1 concentrations were persistently low in treated dogs. We also found that heterozygous GSD-Ia carrier dogs had decreased serum IGF 1, adult body weights and bone dimensions compared to wild-type littermates. In sum, these findings suggest that growth failure in GSD-Ia results, at least in part, from hepatic GH resistance. In addition, gene therapy improved growth in addition to promoting long-term survival in dogs and mice with GSD-Ia.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Supplementary data to this article can be found online at
Figures

References
-
- Koeberl DD, Kishnani PS, Bali D, Chen YT. Emerging therapies for glycogen storage disease type I. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2009;20:252–258. - PubMed
-
- Weinstein DA, Wolfsdorf JI. Effect of continuous glucose therapy with uncooked cornstarch on the long-term clinical course of type 1a glycogen storage disease. Eur J Pediatr. 2002;161(Suppl 1):S35–S39. - PubMed
-
- Melis D, Pivonello R, Parenti G, Della Casa R, Salerno M, Balivo F, Piccolo P, Di Somma C, Colao A, Andria G. The growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor axis in glycogen storage disease type 1: evidence of different growth patterns and insulin-like growth factor levels in patients with glycogen storage disease type 1a and 1b. J Pediatr-Us. 2010;156 (663-U198) - PubMed
-
- Rake JP, Visser G, Labrune P, Leonard JV, Ullrich K, Smit GP. Glycogen storage disease type I: diagnosis, management, clinical course and outcome. Results of the European Study on Glycogen Storage Disease Type I (ESGSD I) Eur J Pediatr. 2002;161(Suppl 1):S20–S34. - PubMed
-
- Mundy HR, Hindmarsh PC, Matthews DR, Leonard JV, Lee PJ. The regulation of growth in glycogen storage disease type 1. Clin Endocrinol. 2003;58:332–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

