Architecture of human translation initiation factor 3
- PMID: 23623729
- PMCID: PMC3739965
- DOI: 10.1016/j.str.2013.04.002
Architecture of human translation initiation factor 3
Abstract
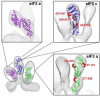
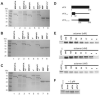
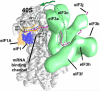
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 3 (eIF3) plays a central role in protein synthesis by organizing the formation of the 43S preinitiation complex. Using genetic tag visualization by electron microscopy, we reveal the molecular organization of ten human eIF3 subunits, including an octameric core. The structure of eIF3 bears a close resemblance to that of the proteasome lid, with a conserved spatial organization of eight core subunits containing PCI and MPN domains that coordinate functional interactions in both complexes. We further show that eIF3 subunits a and c interact with initiation factors eIF1 and eIF1A, which control the stringency of start codon selection. Finally, we find that subunit j, which modulates messenger RNA interactions with the small ribosomal subunit, makes multiple independent interactions with the eIF3 octameric core. These results highlight the conserved architecture of eIF3 and how it scaffolds key factors that control translation initiation in higher eukaryotes, including humans.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Algire MA, Maag D, Lorsch JR. Pi release from eIF2, not GTP hydrolysis, is the step controlled by start-site selection during eukaryotic translation initiation. Mol Cell. 2005;20:251–262. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Shem A, Garreau de Loubresse N, Melnikov S, Jenner L, Yusupova G, Yusupov M. The structure of the eukaryotic ribosome at 3.0 A resolution. Science. 2011;334:1524–1529. - PubMed
-
- Bushell M, Wood W, Clemens MJ, Morley SJ. Changes in integrity and association of eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factors during apoptosis. Eur J Biochem. 2000;267:1083–1091. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

