Tam41 is a CDP-diacylglycerol synthase required for cardiolipin biosynthesis in mitochondria
- PMID: 23623749
- PMCID: PMC3654088
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2013.03.018
Tam41 is a CDP-diacylglycerol synthase required for cardiolipin biosynthesis in mitochondria
Abstract
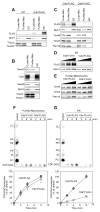
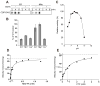
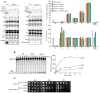
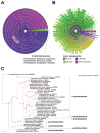
CDP-diacylglycerol (CDP-DAG) is central to the phospholipid biosynthesis pathways in cells. A prevailing view is that only one CDP-DAG synthase named Cds1 is present in both the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial inner membrane (IM) and mediates generation of CDP-DAG from phosphatidic acid (PA) and CTP. However, we demonstrate here by using yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae as a model organism that Cds1 resides in the ER but not in mitochondria, and that Tam41, a highly conserved mitochondrial maintenance protein, directly catalyzes the formation of CDP-DAG from PA in the mitochondrial IM. We also find that inositol depletion by overexpressing an arrestin-related protein Art5 partially restores the defects of cell growth and CL synthesis in the absence of Tam41. The present findings unveil the missing step of the cardiolipin synthesis pathway in mitochondria as well as the flexibile regulation of phospholipid biosynthesis to respond to compromised CDP-DAG synthesis in mitochondria.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Chang SC, Heacock PN, Clancey CJ, Dowhan W. The PEL1 gene (renamed PGS1) encodes the phosphatidylglycero-phosphate synthase of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1998a;273:9829–9836. - PubMed
-
- Chang SC, Heacock PN, Mileykovskaya E, Voelker DR, Dowhan W. Isolation and characterization of the gene (CLS1) encoding cardiolipin synthase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1998b;273:14933–14941. - PubMed
-
- Clancey CJ, Chang SC, Dowhan W. Cloning of a gene (PSD1) encoding phosphatidylserine decarboxylase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae by complementation of an Escherichia coli mutant. J Biol Chem. 1993;268:24580–24590. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

