Salmonella Typhimurium lacking the Znuabc transporter is attenuated and immunogenic in pigs
- PMID: 23623860
- PMCID: PMC3874890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.04.032
Salmonella Typhimurium lacking the Znuabc transporter is attenuated and immunogenic in pigs
Abstract
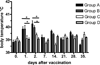
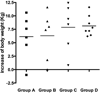
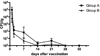
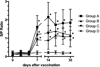
Meat contamination by Salmonella spp. is emerging as a major cause of human enteric infections in industrialized countries. The attempts to reduce human cases of salmonellosis encompass pre- and post-harvest interventions. In this context, vaccination of pigs may represent an effective instrument in eliminating/reducing Salmonella burden through the food chain. We have previously demonstrated that Salmonella Typhimurium lacking the ZnuABC transporter (S. Typhimurium ΔznuABC) is a promising candidate live vaccine in different mouse models of Salmonella Typhimurium infection. In this study, we confirmed in pigs the attenuation of S. Typhimurium ΔznuABC. Moreover, we evaluated the safety and immunogenicity of S. Typhimurium ΔznuABC administered to pigs by the oral route. We monitored clinical conditions of animals and we conducted a microbiological culture and a quantification of the humoral and cellular immune response, respectively, on fecal and blood samples of pigs. After vaccination with attenuated S. Typhimurium ΔznuABC, pigs showed a modest degree of hyperthermia. In addition, fecal shedding of S. Typhimurium ΔznuABC could not be detected 28 days after the inoculum. Furthermore, vaccination with S. Typhimurium ΔznuABC elicited a distinct production of anti-Salmonella antibodies and IFN-γ. Taken together, these results suggest that S. Typhimurium ΔznuABC is attenuated and immunogenic in pigs. Although the vaccine dosages do not guarantee complete safety there is ample margin to set up better conditions of use, suggesting that S. Typhimurium ΔznuABC could be a promising attenuated strain to be used as live mucosal vaccine for oral delivery.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Prime-boost vaccination with attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium ΔznuABC and inactivated Salmonella Choleraesuis is protective against Salmonella Choleraesuis challenge infection in piglets.BMC Vet Res. 2017 Sep 11;13(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12917-017-1202-5. BMC Vet Res. 2017. PMID: 28893256 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium lacking the ZnuABC transporter: an efficacious orally-administered mucosal vaccine against salmonellosis in pigs.Vaccine. 2013 Aug 12;31(36):3695-701. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.05.105. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23770333 Free PMC article.
-
Parenteral administration of attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium ΔznuABC is protective against salmonellosis in piglets.Vaccine. 2014 Jul 7;32(32):4032-8. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.05.066. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Vaccine. 2014. PMID: 24907486
-
Live Attenuated Human Salmonella Vaccine Candidates: Tracking the Pathogen in Natural Infection and Stimulation of Host Immunity.EcoSal Plus. 2016 Nov;7(1):10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0010-2016. doi: 10.1128/ecosalplus.ESP-0010-2016. EcoSal Plus. 2016. PMID: 27809955 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmonella as a vaccine delivery vehicle.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2013 Sep;12(9):1033-45. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2013.825454. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2013. PMID: 24053397 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ptsI gene in the phosphotransfer system is a potential target for developing a live attenuated Salmonella vaccine.Int J Mol Med. 2020 May;45(5):1327-1340. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4505. Epub 2020 Feb 18. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32323733 Free PMC article.
-
Prime-boost vaccination with attenuated Salmonella Typhimurium ΔznuABC and inactivated Salmonella Choleraesuis is protective against Salmonella Choleraesuis challenge infection in piglets.BMC Vet Res. 2017 Sep 11;13(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12917-017-1202-5. BMC Vet Res. 2017. PMID: 28893256 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Zur: Zinc-Sensing Transcriptional Regulator in a Diverse Set of Bacterial Species.Pathogens. 2021 Mar 15;10(3):344. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10030344. Pathogens. 2021. PMID: 33804265 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salmonella enterica Serovar Typhimurium Exploits Inflammation to Modify Swine Intestinal Microbiota.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016 Jan 22;5:106. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2015.00106. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26835435 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuated Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium lacking the ZnuABC transporter: an efficacious orally-administered mucosal vaccine against salmonellosis in pigs.Vaccine. 2013 Aug 12;31(36):3695-701. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2013.05.105. Epub 2013 Jun 13. Vaccine. 2013. PMID: 23770333 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Majowicz SE, Musto J, Scallan E, Angulo FJ, Kirk M, O'Brien SJ, Jones TF, Fazil A, Hoekstra RM. International Collaboration on Enteric Disease 'Burden of Illness' Studies. 2010;50:882–889. - PubMed
-
- Foley SL, Lynne AM. Food animal-associated Salmonella challenges: Pathogenicity and antimicrobial resistance. J Anim Sci. 2008;86:173–187. - PubMed
-
- European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) Pires SM, de Knegt L, Hald T. Estimation of the relative contribution of different food and animal sources to human Salmonella infections in the European Union. 2011 http://www.efsa.europa.eu/en/supporting/doc/184e.pdf.
-
- Eddicks M, Palzer A, Hörmansdorfer S, Ritzmann M, Heinritzi K. Examination of the compatibility of a Salmonella Typhimurium-live vaccine Salmoporc for three day old suckling piglets. Dtsch Tierarztl Wochenschr. 2009;116(7):249–255. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

