Prime-O-glucosylcimifugin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice
- PMID: 23623941
- PMCID: PMC7106058
- DOI: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.04.014
Prime-O-glucosylcimifugin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice
Abstract
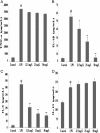
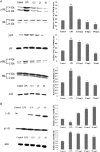
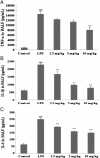
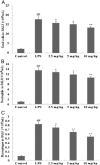
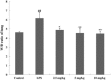
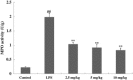
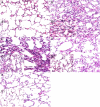
Prime-O-glucosylcimifugin is an active chromone isolated from Saposhnikovia root which has been reported to have various activities, such as anti-convulsant, anticancer, anti-inflammatory properties. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of prime-O-glucosylcimifugin on acute lung injury (ALI) induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. BALB/c mice received intraperitoneal injection of Prime-O-glucosylcimifugin 1h before intranasal instillation (i.n.) of lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Concentrations of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and interleukin (IL)-6 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Pulmonary histological changes were evaluated by hematoxylin-eosin, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity in the lung tissue and lung wet/dry weight ratios were observed. Furthermore, the mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) signaling pathway activation and the phosphorylation of IκBα protein were determined by Western blot analysis. Prime-O-glucosylcimifugin showed promising anti-inflammatory effect by inhibiting the activation of MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathway.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Protective effect of taraxasterol on acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Apr;19(2):342-50. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.01.031. Epub 2014 Feb 15. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24548765
-
Total flavonoids of Mosla scabra leaves attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via down-regulation of inflammatory signaling in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Jul 30;148(3):835-41. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.020. Epub 2013 Jun 6. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23747643
-
Protective effect of cryptotanshinone on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Jan 15;723:494-500. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.10.019. Epub 2013 Oct 24. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24161915
-
Zingerone attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2014 Mar;19(1):103-9. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2013.12.028. Epub 2014 Jan 9. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24412620
-
Preventive and therapeutic effects of Danhong injection on lipopolysaccharide induced acute lung injury in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2013 Aug 26;149(1):352-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2013.06.048. Epub 2013 Jul 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23850708
Cited by
-
Inhibitory Effects of Polydatin on Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated RAW 264.7 Cells.Inflammation. 2015;38(3):1213-20. doi: 10.1007/s10753-014-0087-8. Inflammation. 2015. PMID: 25567371
-
Characterization of metabolites in Saposhnikovia divaricata root from Mongolia.J Nat Med. 2021 Jan;75(1):11-27. doi: 10.1007/s11418-020-01430-9. Epub 2020 Aug 1. J Nat Med. 2021. PMID: 32740706
-
Spiraea prunifolia var. simpliciflora Attenuates Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Responses in a Murine Model of Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury and TNF-α-Stimulated NCI-H292 Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Feb 26;9(3):198. doi: 10.3390/antiox9030198. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32111036 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Medicinal Plants and Their Constituents on Lung Inflammatory Disorders.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2017 Mar 1;25(2):91-104. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2016.187. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2017. PMID: 27956716 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saposhnikovia divaricata-An Ethnopharmacological, Phytochemical and Pharmacological Review.Chin J Integr Med. 2020 Nov;26(11):873-880. doi: 10.1007/s11655-020-3091-x. Epub 2020 Apr 21. Chin J Integr Med. 2020. PMID: 32328867 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mendez J.L., Hubmayr R.D. New insights into the pathology of acute respiratory failure. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2005;11(1):29–36. - PubMed
-
- Kitamura Y., Hashimoto S., Mizuta N., Kobayashi A., Kooguchi K., Fujiwara I. Fas/FasL-dependent apoptosis of alveolar cells after lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2001;163(3 Pt 1):762–769. - PubMed
-
- Rojas M., Woods C.R., Mora A.L., Xu J., Brigham K.L. Endotoxin-induced lung injury in mice: structural, functional, and biochemical responses. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2005;288(2):333–341. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

