Glycogen synthase kinase 3 regulates expression of nuclear factor-erythroid-2 related transcription factor-1 (Nrf1) and inhibits pro-survival function of Nrf1
- PMID: 23623971
- PMCID: PMC4186750
- DOI: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.04.013
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 regulates expression of nuclear factor-erythroid-2 related transcription factor-1 (Nrf1) and inhibits pro-survival function of Nrf1
Abstract
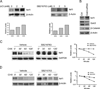
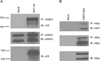
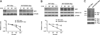
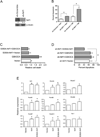
Nuclear factor E2-related factor-1 (Nrf1) is a basic leucine zipper transcription factor that is known to regulate antioxidant and cytoprotective gene expression. It was recently shown that Nrf1 is regulated by SCF-Fbw7 ubiquitin ligase. However our knowledge of upstream signals that targets Nrf1 for degradation by the UPS is not known. We report here that Nrf1 expression is negatively regulated by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) in Fbw7-dependent manner. We show that GSK3 interacts with Nrf1 and phosphorylates the Cdc4 phosphodegron domain (CPD) in Nrf1. Mutation of serine residue in the CPD of Nrf1 to alanine (S350A), blocks Nrf1 from phosphorylation by GSK3, and stabilizes Nrf1. Knockdown of Nrf1 and expression of a constitutively active form of GSK3 results in increased apoptosis in neuronal cells in response to ER stress, while expression of the GSK3 phosphorylation resistant S350A-Nrf1 attenuates apoptotic cell death. Together these data suggest that GSK3 regulates Nrf1 expression and cell survival function in response to stress activation.
Keywords: ARE; CNC-BZIP; CNC-bZIP; CPD; Cap ‘n’ Collar-type basic leucine zipper; Cdc4 phosphodegron domain; ER; Fbw7; GSK3; Nrf1; Nuclear factor E2-related factor-1; SCF; Skp1–Cul1–F-box; Stress response; Transcription factor; UPS; antioxidant response element; endoplasmic reticulum; glycogen synthase kinase 3; nuclear factor E2-related factor-1; ubiquitin proteasome system.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Andrews NC, Erdjument-Bromage H, Davidson MB, Tempst P, Orkin SH, et al. Erythroid transcription factor NF-E2 is a haematopoietic-specific basic-leucine zipper protein. Nature. 1993;362:722–728. - PubMed
-
- Kobayashi A, Ito E, Told T, Kogame K, Takahashi S, Igarashi K, Hayashi N, Yamamoto M, et al. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of a new Cap ‘n’ collar family transcription factor Nrf3. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:6443–6452. - PubMed
-
- Oyake T, Itoh K, Motohashi H, Hayashi N, Hoshino H, Nishizawa M, Yamamoto M, Igarashi K, et al. Bach proteins belong to a novel family of BTB-basic leucine zipper transcription factors that interact with MafK and regulate transcription through the NF-E2 site. Mol. Cell Biol. 1996;16:6083–6095. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

