A perspective on mammalian upstream open reading frame function
- PMID: 23624144
- PMCID: PMC7172355
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.04.020
A perspective on mammalian upstream open reading frame function
Abstract
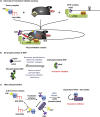
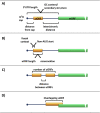
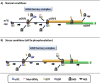
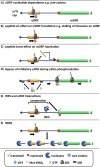
Post-transcriptional control makes a major contribution to the overall regulation of gene expression pathway. Within the cytoplasm this is mediated by a combination of regulatory RNA motifs within the 5' and 3' untranslated regions of mRNAs and their interacting protein/RNA partners. One of the most common regulatory RNA elements in mammalian transcripts (present in approximately 40% of all mRNAs) are upstream open reading frames (uORFs). However, despite the prevalence of these RNA elements how they function is not well understood. In general, they act to repress translation of the physiological ORF under control conditions, and under certain pathophysiological stresses this repression can be alleviated. It is known that re-initiation following the translation of an uORF is utilised in some situations however there are numerous alternative mechanisms that control the synthesis of a protein whose mRNA contains uORFs. Moreover, the trans-acting factors that are also involved in this process are not well defined. In this review we summarise our current understanding of this area and highlight some common features of these RNA motifs that have been discovered to date.
Keywords: 4E-binding proteins; 4EBPs; AdoMetDCS; EMCV; Eif; IRES; NMD; Protein synthesis; RRL; SNP; THPO; Translational control; UTR; Upstream open reading frame; adenosyl-methionine decarboxylase; encephalomyocarditis virus; eukaryotic initiation factor; internal ribosome entry segment; nonsense mediated decay; rabbit reticulocyte lysate; single nucleotide polymorphism; thrombopoietin; uORF; untranslated region; upstream open reading frame.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of plant translation by upstream open reading frames.Plant Sci. 2014 Jan;214:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.09.006. Epub 2013 Sep 18. Plant Sci. 2014. PMID: 24268158 Review.
-
Plant transcripts with long or structured upstream open reading frames in the NDL2 5' UTR can escape nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in a reinitiation-independent manner.J Exp Bot. 2023 Jan 1;74(1):91-103. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erac385. J Exp Bot. 2023. PMID: 36169317
-
Translation reinitiation after uORFs does not fully protect mRNAs from nonsense-mediated decay.RNA. 2023 Jun;29(6):735-744. doi: 10.1261/rna.079525.122. Epub 2023 Mar 6. RNA. 2023. PMID: 36878710 Free PMC article.
-
Polyamine-responsive ribosomal arrest at the stop codon of an upstream open reading frame of the AdoMetDC1 gene triggers nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in Arabidopsis thaliana.Plant Cell Physiol. 2014 Sep;55(9):1556-67. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcu086. Epub 2014 Jun 14. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014. PMID: 24929422
-
Translational Regulation by Upstream Open Reading Frames and Human Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1157:99-116. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-19966-1_5. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31342439 Review.
Cited by
-
The Challenges and Strategies of Antisense Oligonucleotide Drug Delivery.Biomedicines. 2021 Apr 16;9(4):433. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9040433. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 33923688 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Viral and Cellular mRNA Translation in Coronavirus-Infected Cells.Adv Virus Res. 2016;96:165-192. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2016.08.001. Epub 2016 Sep 10. Adv Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27712623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RefSeq: an update on mammalian reference sequences.Nucleic Acids Res. 2014 Jan;42(Database issue):D756-63. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1114. Epub 2013 Nov 19. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014. PMID: 24259432 Free PMC article.
-
Ribosome profiling reveals a cell-type-specific translational landscape in brain tumors.J Neurosci. 2014 Aug 13;34(33):10924-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0084-14.2014. J Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25122893 Free PMC article.
-
Non-coding functions of alternative pre-mRNA splicing in development.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Dec;47-48:32-9. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.10.018. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26493705 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akimoto C., Sakashita E., Kasashima K., Kuroiwa K., Tominaga K., Hamamoto T. Translational repression of the McKusick-Kaufman syndrome transcript by unique upstream open reading frames encoding mitochondrial proteins with alternative polyadenylation sites. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. 2012 epub pii: S0304-4165(12)00356-X. - PubMed
-
- Blagden S.P., Willis A.E. The biological and therapeutic relevance of mRNA translation in cancer. Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology. 2011;8:280–291. - PubMed
-
- Brown C.Y., Mize G.J., Pineda M., George D.L., Morris D.R. Role of two upstream open reading frames in the translational control of oncogene mdm2. Oncogene. 1999;18:5631–5637. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

