Forced swim-induced musculoskeletal hyperalgesia is mediated by CRF2 receptors but not by TRPV1 receptors
- PMID: 23624287
- PMCID: PMC3696409
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.016
Forced swim-induced musculoskeletal hyperalgesia is mediated by CRF2 receptors but not by TRPV1 receptors
Abstract
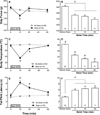
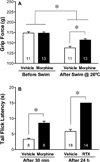
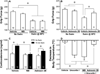
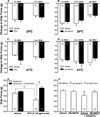
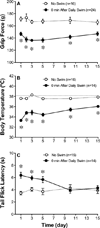
The exacerbation of musculoskeletal pain by stress in humans is modeled by the musculoskeletal hyperalgesia in rodents following a forced swim. We hypothesized that stress-sensitive corticotropin releasing factor (CRF) receptors and transient receptor vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) receptors are responsible for the swim stress-induced musculoskeletal hyperalgesia. We confirmed that a cold swim (26 °C) caused a transient, morphine-sensitive decrease in grip force responses reflecting musculoskeletal hyperalgesia in mice. Pretreatment with the CRF2 receptor antagonist astressin 2B, but not the CRF1 receptor antagonist NBI-35965, attenuated this hyperalgesia. Desensitizing the TRPV1 receptor centrally or peripherally using desensitizing doses of resiniferatoxin (RTX) failed to prevent the musculoskeletal hyperalgesia produced by cold swim. SB-366791, a TRPV1 antagonist, also failed to influence swim-induced hyperalgesia. Together these data indicate that swim stress-induced musculoskeletal hyperalgesia is mediated, in part, by CRF2 receptors but is independent of the TRPV1 receptor.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Chung MK, Jung SJ, Oh SB. Role of TRP channels in pain sensation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2011;704:615–636. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

