Inhibition of ROS-activated p38MAPK pathway is involved in the protective effect of H2S against chemical hypoxia-induced inflammation in PC12 cells
- PMID: 23624824
- PMCID: PMC3671109
- DOI: 10.1007/s11064-013-1044-x
Inhibition of ROS-activated p38MAPK pathway is involved in the protective effect of H2S against chemical hypoxia-induced inflammation in PC12 cells
Abstract
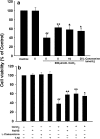
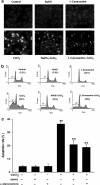
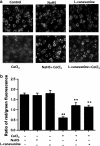
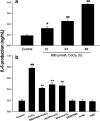
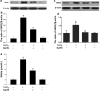
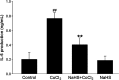
We have demonstrated the neuroprotection of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) against chemical hypoxia-induced injury by inhibiting p38MAPK pathway. The present study attempts to evaluate the effect of H2S on chemical hypoxia-induced inflammation responses and its mechanisms in PC12 cells. We found that treatment of PC12 cells with cobalt chloride (CoCl2, a hypoxia mimetic agent) enhanced IL-6 secretion, nitric oxide (NO) generation and expression levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS). L-canavanine, a selective iNOS inhibitor, partly blocked CoCl2-induced cytotoxicity, apoptosis and mitochondrial insult. In addition, 7-Nitroindazole (7-NI), an inhibitor of nNOS, also partly attenuated the CoCl2-induced cytotoxicity. The inhibition of p38MAPK by SB203580 (a selective p38MAPK inhibitor) or genetic silencing of p38MAPK by RNAi (Si-p38) depressed not only CoCl2-induced iNOS expression, NO production, but also IL-6 secretion. In addition, N-acetyl-L-cysteine, a reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenger, conferred a similar protective effect of SB203580 or Si-p38 against CoCl2-induced inflammatory responses. Importantly, pretreatment of PC12 cells with exogenous application of sodium hydrosulfide (a H2S donor, 400 μmol/l) for 30 min before exposure to CoCl2 markedly attenuated chemical hypoxia-stimulated iNOS and nNOS expression, NO generation and IL-6 secretion as well as p38MAPK phosphorylation in PC12 cells. Taken together, we demonstrated that p38MAPK-iNOS pathway contributes to chemical hypoxia-induced inflammation and that H2S produces an anti-inflammatory effect in chemical hypoxia-stimulated PC12 cells, which may be partly due to inhibition of ROS-activated p38MAPK-iNOS pathway.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hydrogen sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced injury by inhibiting ROS-activated ERK1/2 and p38MAPK signaling pathways in PC12 cells.PLoS One. 2011;6(10):e25921. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0025921. Epub 2011 Oct 5. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21998720 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous hydrogen sulfide protects against doxorubicin-induced inflammation and cytotoxicity by inhibiting p38MAPK/NFκB pathway in H9c2 cardiac cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(6):1668-80. doi: 10.1159/000356602. Epub 2013 Dec 13. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2013. PMID: 24356372
-
Interaction between ROS and p38MAPK contributes to chemical hypoxia-induced injuries in PC12 cells.Mol Med Rep. 2012 Jan;5(1):250-5. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2011.623. Epub 2011 Oct 11. Mol Med Rep. 2012. PMID: 21993612
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in secondary neuronal injury.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24239876 Review.
-
Research progress of p38 as a new therapeutic target against morphine tolerance and the current status of therapy of morphine tolerance.J Drug Target. 2023 Feb;31(2):152-165. doi: 10.1080/1061186X.2022.2138895. Epub 2022 Nov 2. J Drug Target. 2023. PMID: 36264036 Review.
Cited by
-
Luminescent gold nanocluster-based sensing platform for accurate H2S detection in vitro and in vivo with improved anti-interference.Light Sci Appl. 2017 Dec 1;6(12):e17107. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2017.107. eCollection 2017 Dec. Light Sci Appl. 2017. PMID: 30167221 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of intermittent hypoxia on neuro-functional recovery post brain ischemia in mice.J Mol Neurosci. 2015 Apr;55(4):923-30. doi: 10.1007/s12031-014-0447-8. Epub 2014 Oct 26. J Mol Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25344154
-
Pre- and posttreatment with hydrogen sulfide prevents ventilator-induced lung injury by limiting inflammation and oxidation.PLoS One. 2017 Apr 28;12(4):e0176649. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176649. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28453540 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of Xuebijing injection on paraquat-induced pulmonary injury via down-regulating the expression of p38 MAPK in rats.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 16;14:498. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-498. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25511395 Free PMC article.
-
Key Role of ROS in the Process of 15-Lipoxygenase/15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoiccid-Induced Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling in Hypoxia Pulmonary Hypertension.PLoS One. 2016 Feb 12;11(2):e0149164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0149164. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 26871724 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

