Coordinated conformational and compositional dynamics drive ribosome translocation
- PMID: 23624862
- PMCID: PMC3883222
- DOI: 10.1038/nsmb.2567
Coordinated conformational and compositional dynamics drive ribosome translocation
Abstract
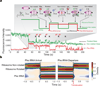
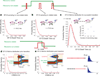
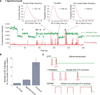
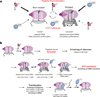
During translation elongation, the ribosome compositional factors elongation factor G (EF-G; encoded by fusA) and tRNA alternately bind to the ribosome to direct protein synthesis and regulate the conformation of the ribosome. Here, we use single-molecule fluorescence with zero-mode waveguides to directly correlate ribosome conformation and composition during multiple rounds of elongation at high factor concentrations in Escherichia coli. Our results show that EF-G bound to GTP (EF-G-GTP) continuously samples both rotational states of the ribosome, binding with higher affinity to the rotated state. Upon successful accommodation into the rotated ribosome, the EF-G-ribosome complex evolves through several rate-limiting conformational changes and the hydrolysis of GTP, which results in a transition back to the nonrotated state and in turn drives translocation and facilitates release of both EF-G-GDP and E-site tRNA. These experiments highlight the power of tracking single-molecule conformation and composition simultaneously in real time.
Figures




References
-
- Blanchard SC, Gonzalez RL, Kim HD, Chu S, Puglisi JD. tRNA selection and kinetic proofreading in translation. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2004;11:1008–1014. - PubMed
-
- Rodnina MV, Savelsbergh A, Katunin VI, Wintermeyer W. Hydrolysis of GTP by elongation factor G drives tRNA movement on the ribosome. Nature. 1997;385:37–41. - PubMed
-
- Valle M, et al. Locking and unlocking of ribosomal motions. Cell. 2003;114:123–134. - PubMed
-
- Spirin AS. A model of the functioning ribosome: locking and unlocking of the ribosome subparticles. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1969;34:197–207. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

