MEK inhibition affects STAT3 signaling and invasion in human melanoma cell lines
- PMID: 23624919
- PMCID: PMC3769503
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2013.131
MEK inhibition affects STAT3 signaling and invasion in human melanoma cell lines
Abstract
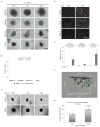
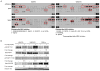
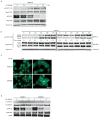
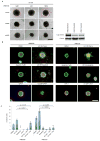
Elevated activity of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling cascade is found in the majority of human melanomas and is known to regulate proliferation, survival and invasion. Current targeted therapies focus on decreasing the activity of this pathway; however, we do not fully understand how these therapies impact tumor biology, especially given that melanoma is a heterogeneous disease. Using a three-dimensional (3D), collagen-embedded spheroid melanoma model, we observed that MEK and BRAF inhibitors can increase the invasive potential of ∼20% of human melanoma cell lines. The invasive cell lines displayed increased receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) activity and activation of the Src/FAK/signal transducers and activators of transcription-3 (STAT3) signaling axis, also associated with increased cell-to-cell adhesion and cadherin engagement following MEK inhibition. Targeting various RTKs, Src, FAK and STAT3 with small molecule inhibitors in combination with a MEK inhibitor prevented the invasive phenotype, but only STAT3 inhibition caused cell death in the 3D context. We further show that STAT3 signaling is induced in BRAF-inhibitor-resistant cells. Our findings suggest that MEK and BRAF inhibitors can induce STAT3 signaling, causing potential adverse effects such as increased invasion. We also provide the rationale for the combined targeting of the MAPK pathway along with inhibitors of RTKs, SRC or STAT3 to counteract STAT3-mediated resistance phenotypes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

