Patients with hepatitis C infection and normal liver function: an evaluation of cognitive function
- PMID: 23625064
- PMCID: PMC3717602
- DOI: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2012-131185
Patients with hepatitis C infection and normal liver function: an evaluation of cognitive function
Abstract
Purpose of the study: Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is associated with neuropsychiatric complaints. Previous studies have associated cognitive alterations with HCV infection but have often included confounding factors in their samples. This study compares the cognitive performance between patients with HCV infection (HCV patients) and a control group while excluding other factors that may cause cognitive impairment.
Study design: This cross-sectional study was conducted from March 2010 through June 2011. HCV infected patients and healthy individuals between the ages of 18 and 80 years were considered eligible. The exclusion criteria included well established causes of cognitive impairment such as depression and cirrhosis. Study participants underwent neuropsychological testing involving measures of attention, memory, abstraction, visuoconstructive abilities, and executive function.
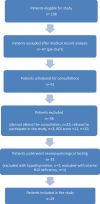
Results: Of 138 initial patients, 47 were excluded because of their medical records, three refused to participate, 23 did not attend the consultation, and 32 were excluded because of having Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) scores >11. In all, 33 patients underwent neuropsychological testing; however, three were excluded because of having hypothyroidism, and one was excluded because of having a cobalamin deficiency. For the control group, of the 33 healthy individuals that were selected, four were excluded because of having BDI scores >11. Thus, the final analysis included 29 HCV patients and 29 control participants. The groups did not differ in education, age, or gender. No statistically significant differences were found between the groups regarding cognitive performance.
Conclusions: In this study using strict selection criteria, there was no evidence of an association between HCV infection and cognitive impairment.
Keywords: INFECTIOUS DISEASES; NEUROLOGY.
Figures
References
-
- Lauer GM, Walker BD. Hepatitis C virus infection. N Engl J Med 2001;345:41–52 - PubMed
-
- Houghton M. Discovery of the hepatitis C virus. Liver Int 2009;29:82–8 - PubMed
-
- Zignego AL, Ferri C, Pileri SA, et al. Extrahepatic manifestations of hepatitis C virus infection: a general overview and guidelines for a clinical approach. Dig Liver Dis 2007;39:2–17 - PubMed
-
- Galossi A, Guarisco R, Bellis L, et al. Extrahepatic manifestations of chronic HCV infection. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis 2007;16:65–73 - PubMed
-
- Weissenborn K, Bokemeyer M, Krause J, et al. Neurological and neuropsychiatric syndromes associated with liver disease. AIDS 2005;19:S93–8 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

