FUS/TLS assembles into stress granules and is a prosurvival factor during hyperosmolar stress
- PMID: 23625794
- PMCID: PMC4000275
- DOI: 10.1002/jcp.24395
FUS/TLS assembles into stress granules and is a prosurvival factor during hyperosmolar stress
Abstract
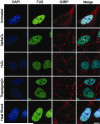
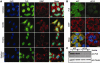
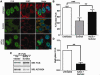
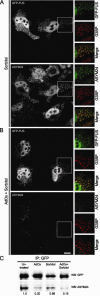
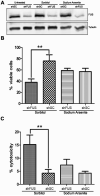
FUsed in Sarcoma/Translocated in LipoSarcoma (FUS/TLS or FUS) has been linked to several biological processes involving DNA and RNA processing, and has been associated with multiple diseases, including myxoid liposarcoma and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). ALS-associated mutations cause FUS to associate with stalled translational complexes called stress granules under conditions of stress. However, little is known regarding the normal role of endogenous (non-disease linked) FUS in cellular stress response. Here, we demonstrate that endogenous FUS exerts a robust response to hyperosmolar stress induced by sorbitol. Hyperosmolar stress causes an immediate re-distribution of nuclear FUS to the cytoplasm, where it incorporates into stress granules. The redistribution of FUS to the cytoplasm is modulated by methyltransferase activity, whereas the inhibition of methyltransferase activity does not affect the incorporation of FUS into stress granules. The response to hyperosmolar stress is specific, since endogenous FUS does not redistribute to the cytoplasm in response to sodium arsenite, hydrogen peroxide, thapsigargin, or heat shock, all of which induce stress granule assembly. Intriguingly, cells with reduced expression of FUS exhibit a loss of cell viability in response to sorbitol, indicating a prosurvival role for endogenous FUS in the cellular response to hyperosmolar stress.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Alfieri RR, Petronini PG. Hyperosmotic stress response: comparison with other cellular stresses. Pflugers Arch. 2007;454(2):173–185. - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. Stress granules: the Tao of RNA triage. Trends Biochem Sci. 2008;33(3):141–150. - PubMed
-
- Anderson P, Kedersha N. Stress granules. Curr Biol. 2009;19(10):R397–398. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

