Store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) induced by protease-activated receptor-1 mediates STIM1 protein phosphorylation to inhibit SOCE in endothelial cells through AMP-activated protein kinase and p38β mitogen-activated protein kinase
- PMID: 23625915
- PMCID: PMC3675634
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.411272
Store-operated Ca2+ entry (SOCE) induced by protease-activated receptor-1 mediates STIM1 protein phosphorylation to inhibit SOCE in endothelial cells through AMP-activated protein kinase and p38β mitogen-activated protein kinase
Abstract
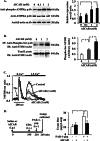
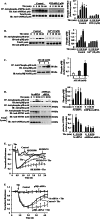
The Ca(2+) sensor STIM1 is crucial for activation of store-operated Ca(2+) entry (SOCE) through transient receptor potential canonical and Orai channels. STIM1 phosphorylation serves as an "off switch" for SOCE. However, the signaling pathway for STIM1 phosphorylation is unknown. Here, we show that SOCE activates AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK); its effector p38β mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38β MAPK) phosphorylates STIM1, thus inhibiting SOCE in human lung microvascular endothelial cells. Activation of AMPK using 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-β-d-ribofuranoside (AICAR) resulted in STIM1 phosphorylation on serine residues and prevented protease-activated receptor-1 (PAR-1)-induced Ca(2+) entry. Furthermore, AICAR pretreatment blocked PAR-1-induced increase in the permeability of mouse lung microvessels. Activation of SOCE with thrombin caused phosphorylation of isoform α1 but not α2 of the AMPK catalytic subunit. Moreover, knockdown of AMPKα1 augmented SOCE induced by thrombin. Interestingly, SB203580, a selective inhibitor of p38 MAPK, blocked STIM1 phosphorylation and led to sustained STIM1-puncta formation and Ca(2+) entry. Of the three p38 MAPK isoforms expressed in endothelial cells, p38β knockdown prevented PAR-1-mediated STIM1 phosphorylation and potentiated SOCE. In addition, inhibition of the SOCE downstream target CaM kinase kinase β (CaMKKβ) or knockdown of AMPKα1 suppressed PAR-1-mediated phosphorylation of p38β and hence STIM1. Thus, our findings demonstrate that SOCE activates CaMKKβ-AMPKα1-p38β MAPK signaling to phosphorylate STIM1, thereby suppressing endothelial SOCE and permeability responses.
Keywords: AMP-activated Kinase (AMPK); Calcium Channels; Endothelial Dysfunction; Phosphorylation; Protease-activated Receptor-1; Store-operated Calcium Entry; Stromal Interaction Molecule-1; Thrombin; Vascular Permeability; p38 MAPK.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Pyk2 phosphorylation of VE-PTP downstream of STIM1-induced Ca2+ entry regulates disassembly of adherens junctions.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Jun 1;312(6):L1003-L1017. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00008.2017. Epub 2017 Apr 6. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28385807 Free PMC article.
-
Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptors Potentiate 5'-Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Stimulation and Glucose Uptake Triggered by Thapsigargin-Induced Store-Operated Ca2+ Entry in Human Neuroblastoma Cells.Neurochem Res. 2018 Feb;43(2):245-258. doi: 10.1007/s11064-017-2410-x. Epub 2017 Oct 9. Neurochem Res. 2018. PMID: 28994003
-
STIM1 Phosphorylation at Y361 Recruits Orai1 to STIM1 Puncta and Induces Ca2+ Entry.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 20;7:42758. doi: 10.1038/srep42758. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28218251 Free PMC article.
-
Key components of store-operated Ca2+ entry in non-excitable cells.J Pharmacol Sci. 2014;125(4):340-6. doi: 10.1254/jphs.14r06cp. Epub 2014 Jul 17. J Pharmacol Sci. 2014. PMID: 25030742 Review.
-
Regulation of Orai1/STIM1 by the kinases SGK1 and AMPK.Cell Calcium. 2012 Nov;52(5):347-54. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2012.05.005. Epub 2012 Jun 7. Cell Calcium. 2012. PMID: 22682960 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel role of the ER/SR Ca2+ sensor STIM1 in the regulation of cardiac metabolism.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 May 1;316(5):H1014-H1026. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00544.2018. Epub 2018 Dec 21. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30575437 Free PMC article.
-
AMP-Activated Protein Kinase (AMPK)-Dependent Regulation of Renal Transport.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Nov 6;19(11):3481. doi: 10.3390/ijms19113481. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30404151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deubiquitinase function of A20 maintains and repairs endothelial barrier after lung vascular injury.Cell Death Discov. 2018 May 16;4:60. doi: 10.1038/s41420-018-0056-3. eCollection 2018. Cell Death Discov. 2018. PMID: 29796309 Free PMC article.
-
p38 MAPK activation and STIM1-Orai3 association mediate TRPC6 externalization.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023 Jun 1;324(6):C1199-C1212. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00425.2022. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37093037 Free PMC article.
-
The interplay between mitochondria and store-operated Ca2+ entry: Emerging insights into cardiac diseases.J Cell Mol Med. 2021 Oct;25(20):9496-9512. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.16941. Epub 2021 Sep 26. J Cell Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34564947 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Tiruppathi C., Ahmmed G. U., Vogel S. M., Malik A. B. (2006) Ca2+ signaling, TRP channels, and endothelial permeability. Microcirculation 13, 693–708 - PubMed
-
- Nilius B., Droogmans G. (2001) Ion channels and their functional role in vascular endothelium. Physiol. Rev. 81, 1415–1459 - PubMed
-
- Sundivakkam P. C., Freichel M., Singh V., Yuan J. P., Vogel S. M., Flockerzi V., Malik A. B., Tiruppathi C. (2012) The Ca2+ sensor stromal interaction molecule 1 (STIM1) is necessary and sufficient for the store-operated Ca2+ entry function of transient receptor potential canonical (TRPC) 1 and 4 channels in endothelial cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 81, 510–526 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Li J., Cubbon R. M., Wilson L. A., Amer M. S., McKeown L., Hou B., Majeed Y., Tumova S., Seymour V. A., Taylor H., Stacey M., O'Regan D., Foster R., Porter K. E., Kearney M. T., Beech D. J. (2011) Orai1 and CRAC channel dependence of VEGF-activated Ca2+ entry and endothelial tube formation. Circ. Res. 108, 1190–1198 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

