Engineering A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP)-selective regulatory subunits of protein kinase A (PKA) through structure-based phage selection
- PMID: 23625929
- PMCID: PMC3682517
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.447326
Engineering A-kinase anchoring protein (AKAP)-selective regulatory subunits of protein kinase A (PKA) through structure-based phage selection
Abstract
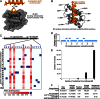
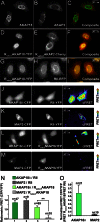
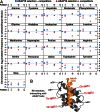
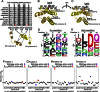
PKA is retained within distinct subcellular environments by the association of its regulatory type II (RII) subunits with A-kinase anchoring proteins (AKAPs). Conventional reagents that universally disrupt PKA anchoring are patterned after a conserved AKAP motif. We introduce a phage selection procedure that exploits high-resolution structural information to engineer RII mutants that are selective for a particular AKAP. Selective RII (RSelect) sequences were obtained for eight AKAPs following competitive selection screening. Biochemical and cell-based experiments validated the efficacy of RSelect proteins for AKAP2 and AKAP18. These engineered proteins represent a new class of reagents that can be used to dissect the contributions of different AKAP-targeted pools of PKA. Molecular modeling and high-throughput sequencing analyses revealed the molecular basis of AKAP-selective interactions and shed new light on native RII-AKAP interactions. We propose that this structure-directed evolution strategy might be generally applicable for the investigation of other protein interaction surfaces.
Keywords: AKAP; Cell Biology; Compartmentalization; Peptide Arrays; Phage Display; Protein Kinase A (PKA); Structure-based Design.
Figures


References
-
- Roy J., Cyert M. S. (2009) Cracking the phosphatase code: docking interactions determine substrate specificity. Sci. Signal. 2, re9. - PubMed
-
- Gold M. G., Barford D., Komander D. (2006) Lining the pockets of kinases and phosphatases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 16, 693–701 - PubMed
-
- Gold M. G., Lygren B., Dokurno P., Hoshi N., McConnachie G., Taskén K., Carlson C. R., Scott J. D., Barford D. (2006) Molecular basis of AKAP specificity for PKA regulatory subunits. Mol. Cell 24, 383–395 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

