Multi-chromatic control of mammalian gene expression and signaling
- PMID: 23625964
- PMCID: PMC3695509
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt340
Multi-chromatic control of mammalian gene expression and signaling
Abstract
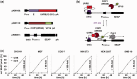
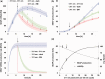
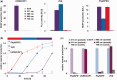
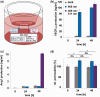
The emergence and future of mammalian synthetic biology depends on technologies for orchestrating and custom tailoring complementary gene expression and signaling processes in a predictable manner. Here, we demonstrate for the first time multi-chromatic expression control in mammalian cells by differentially inducing up to three genes in a single cell culture in response to light of different wavelengths. To this end, we developed an ultraviolet B (UVB)-inducible expression system by designing a UVB-responsive split transcription factor based on the Arabidopsis thaliana UVB receptor UVR8 and the WD40 domain of COP1. The system allowed high (up to 800-fold) UVB-induced gene expression in human, monkey, hamster and mouse cells. Based on a quantitative model, we determined critical system parameters. By combining this UVB-responsive system with blue and red light-inducible gene control technology, we demonstrate multi-chromatic multi-gene control by differentially expressing three genes in a single cell culture in mammalian cells, and we apply this system for the multi-chromatic control of angiogenic signaling processes. This portfolio of optogenetic tools enables the design and implementation of synthetic biological networks showing unmatched spatiotemporal precision for future research and biomedical applications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of Arabidopsis gene expression by low fluence rate UV-B independently of UVR8 and stress signaling.Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2019 Jul 10;18(7):1675-1684. doi: 10.1039/c9pp00151d. Photochem Photobiol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31218318
-
The C-terminal 17 amino acids of the photoreceptor UVR8 is involved in the fine-tuning of UV-B signaling.J Integr Plant Biol. 2020 Sep;62(9):1327-1340. doi: 10.1111/jipb.12977. Epub 2020 Jul 17. J Integr Plant Biol. 2020. PMID: 32492260
-
Perception and Signaling of Ultraviolet-B Radiation in Plants.Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2021 Jun 17;72:793-822. doi: 10.1146/annurev-arplant-050718-095946. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2021. PMID: 33636992 Review.
-
UV-B induction of the E3 ligase ARIADNE12 depends on CONSTITUTIVELY PHOTOMORPHOGENIC 1.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2015 Aug;93:18-28. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2015.03.006. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2015. PMID: 25817546 Free PMC article.
-
Cooling Down Thermomorphogenesis by UV-B Signaling.Trends Plant Sci. 2017 Jun;22(6):447-449. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Trends Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28438558 Review.
Cited by
-
Automated optogenetic feedback control for precise and robust regulation of gene expression and cell growth.Nat Commun. 2016 Aug 26;7:12546. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12546. Nat Commun. 2016. PMID: 27562138 Free PMC article.
-
Control of gene expression using a red- and far-red light-responsive bi-stable toggle switch.Nat Protoc. 2014 Mar;9(3):622-32. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2014.038. Epub 2014 Feb 20. Nat Protoc. 2014. PMID: 24556785
-
Near-infrared light-controlled systems for gene transcription regulation, protein targeting and spectral multiplexing.Nat Protoc. 2018 May;13(5):1121-1136. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2018.022. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Nat Protoc. 2018. PMID: 29700485 Free PMC article.
-
How to Train a Cell-Cutting-Edge Molecular Tools.Front Chem. 2017 Mar 10;5:12. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2017.00012. eCollection 2017. Front Chem. 2017. PMID: 28344971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A light way for nuclear cell biologists.J Biochem. 2021 Apr 18;169(3):273-286. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvaa139. J Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33245128 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Deans TL, Cantor CR, Collins JJ. A tunable genetic switch based on RNAi and repressor proteins for regulating gene expression in mammalian cells. Cell. 2007;130:363–372. - PubMed
-
- Kramer BP, Viretta AU, Daoud-El-Baba M, Aubel D, Weber W, Fussenegger M. An engineered epigenetic transgene switch in mammalian cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004;22:867–870. - PubMed
-
- Tigges M, Marquez-Lago TT, Stelling J, Fussenegger M. A tunable synthetic mammalian oscillator. Nature. 2009;457:309–312. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

