Update on the management of cirrhosis - focus on cost-effective preventative strategies
- PMID: 23626470
- PMCID: PMC3632499
- DOI: 10.2147/CEOR.S30675
Update on the management of cirrhosis - focus on cost-effective preventative strategies
Abstract
Cirrhosis is a chronic liver disease stage that encompasses a variety of etiologies resulting in liver damage. This damage may induce secondary complications such as portal hypertension, esophageal variceal bleeding, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis, and hepatic encephalopathy. Screening for and management of these complications incurs substantial health care costs; thus, determining the most economical and beneficial treatment strategies is essential. This article reviews the economic impact of a variety of prophylactic and treatment regimens employed for cirrhosis-related complications. Prophylactic use of β-adrenergic blockers for portal hypertension and variceal bleeding appears to be cost-effective, but the most economical regimen for treatment of initial bleeding is unclear given that cost comparisons of pharmacologic and surgical regimens are lacking. In contrast, prophylaxis for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis cannot be recommended. Standard therapy for spontaneous bacterial peritonitis includes antibiotics, and the overall economic impact of these medications depends largely on their direct cost. However, the potential development of bacterial antibiotic resistance and resulting clinical failure should also be considered. Nonabsorbable disaccharides are standard therapies for hepatic encephalopathy; however, given their questionable efficacy, the nonsystemic antibiotic rifaximin may be a more cost-effective, long-term treatment for hepatic encephalopathy, despite its increased direct cost, because of its demonstrated efficacy and prevention of hospitalization. Further studies evaluating the cost burden of cirrhosis and cirrhosis-related complications, including screening costs, the cost of treatment and maintenance therapy, conveyance to liver transplantation, liver transplantation success, and health-related quality of life after transplantation, are essential for evaluation of the economic burden of hepatic encephalopathy and all cirrhosis-related complications.
Keywords: cost; hepatic encephalopathy; lactulose; maintenance of remission; rifaximin.
Figures
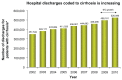
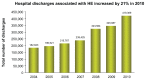
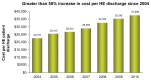
References
-
- Heidelbaugh JJ, Bruderly M. Cirrhosis and chronic liver failure: part I. Diagnosis and evaluation. Am Fam Physician. 2006;74(5):756–762. - PubMed
-
- Garcia-Tsao G, Lim JK. Management and treatment of patients with cirrhosis and portal hypertension: recommendations from the Department of Veterans Affairs Hepatitis C Resource Center Program and the National Hepatitis C Program. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104(7):1802–1829. - PubMed
-
- Cardenas A, Gines P. Management of complications of cirrhosis in patients awaiting liver transplantation. J Hepatol. 2005;42(Suppl 1):S124–S133. - PubMed
-
- Lim YS, Kim WR. The global impact of hepatic fibrosis and end-stage liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2008;12(4):733–746. vii. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

