Oxytocin ameliorates remote liver injury induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion in rats
- PMID: 23626480
- PMCID: PMC3634095
- DOI: 10.4196/kjpp.2013.17.2.169
Oxytocin ameliorates remote liver injury induced by renal ischemia-reperfusion in rats
Abstract
Renal ischemia-reperfusion (IR) causes remote liver damage. Oxytocin has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. The main purpose of this study was to evaluate the protective function of oxytocin (OT) in remote liver damage triggered by renal IR in rats. Twenty four rats were randomly divided into four different groups, each containing 8 rats. The groups were as follows: (1) Sham operated group; (2) Sham operated+OT group (3) Renal IR group; (4) Renal IR+OT group. OT (500µg/kg) was administered subcutaneously 12 and 24 hours before and immediately after ischemia. At the end of experimental procedure, the rats were sacrificed, and liver specimens were taken for histological assessment or determination of malondialdehyde (MDA), total oxidant status (TOS), total antioxidant status (TAS), paraoxonase (PON-1) activity and nitric oxide (NO). The results showed that renal IR injury constituted a notable elevation in MDA, TOS, Oxidative stress index (OSI) and significantly decreased TAS, PON-1 actvity and NO in liver tissue (p<0.05). Additionally renal IR provoked significant augmentation in hepatic microscopic damage scores. However, alterations in these biochemical and histopathological indices due to IR injury were attenuated by OT treatment (p<0.05). These findings show that OT ameliorates remote liver damage triggered by renal ischemia-reperfusion and this preservation involves suppression of inflammation and regulation of oxidant-antioxidant status.
Keywords: Inflammation; Ischemia-reperfusion; Oxidative stress; Oxytocin; Remote liver injury.
Figures
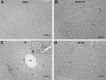
References
-
- Serteser M, Koken T, Kahraman A, Yilmaz K, Akbulut G, Dilek ON. Changes in hepatic TNF-alpha levels, antioxidant status, and oxidation products after renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. J Surg Res. 2002;107:234–240. - PubMed
-
- Miyazawa S, Watanabe H, Miyaji C, Hotta O, Abo T. Leukocyte accumulation and changes in extra-renal organs during renal ischemia reperfusion in mice. J Lab Clin Med. 2002;139:269–278. - PubMed
-
- Kaçmaz A, User EY, Sehirli AO, Tilki M, Ozkan S, Sener G. Protective effect of melatonin against ischemia/reperfusion-induced oxidative remote organ injury in the rat. Surg Today. 2005;35:744–750. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

