Design and development of synthetic microbial platform cells for bioenergy
- PMID: 23626588
- PMCID: PMC3630320
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00092
Design and development of synthetic microbial platform cells for bioenergy
Abstract
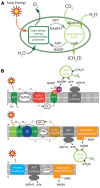
The finite reservation of fossil fuels accelerates the necessity of development of renewable energy sources. Recent advances in synthetic biology encompassing systems biology and metabolic engineering enable us to engineer and/or create tailor made microorganisms to produce alternative biofuels for the future bio-era. For the efficient transformation of biomass to bioenergy, microbial cells need to be designed and engineered to maximize the performance of cellular metabolisms for the production of biofuels during energy flow. Toward this end, two different conceptual approaches have been applied for the development of platform cell factories: forward minimization and reverse engineering. From the context of naturally minimized genomes,non-essential energy-consuming pathways and/or related gene clusters could be progressively deleted to optimize cellular energy status for bioenergy production. Alternatively, incorporation of non-indigenous parts and/or modules including biomass-degrading enzymes, carbon uptake transporters, photosynthesis, CO2 fixation, and etc. into chassis microorganisms allows the platform cells to gain novel metabolic functions for bioenergy. This review focuses on the current progress in synthetic biology-aided pathway engineering in microbial cells and discusses its impact on the production of sustainable bioenergy.
Keywords: bioenergy; genome reduction; metabolic engineering; microbial platform cells; synthetic biology.
Figures
References
-
- Ara K., Ozaki K., Nakamura K., Yamane K., Sekiguchi J., Ogasawara N. (2007). Bacillus minimum genome factory: effective utilization of microbial genome information. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 46 169–178 - PubMed
-
- Atsumi S., Hanai T., Liao J. C. (2008). Non-fermentative pathways for synthesis of branched-chain higher alcohols as biofuels. Nature 451 86–89 - PubMed
-
- Averhoff B. (2009). Shuffling genes around in hot environments: the unique DNA transporter of Thermus thermophilus. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 33 611–626 - PubMed
-
- Barber J. (2009). Photosynthetic energy conversion: natural and artificial. Chem. Soc. Rev. 38 185–196 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

